Greenhouse Gases Definition Environmental Science

Explaining The Greenhouse Effect Sustainability Youtube
What Is Methane Methane Greenhouse Gas Facts
.png)
Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
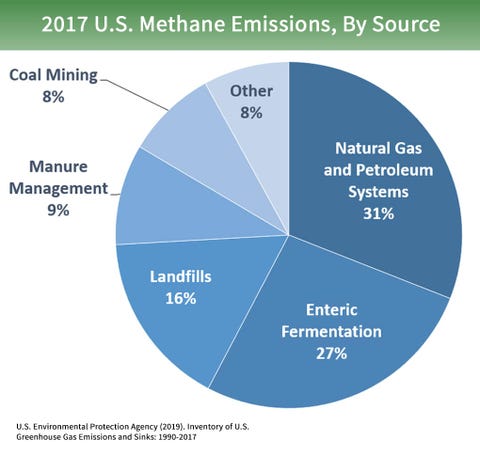
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Eia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Overview
However, the buildup of greenhouse gases can change Earth's climate and result in dangerous effects to human health and welfare and to.

Greenhouse gases definition environmental science. (To a lesser extent, surface-level ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases also trap infrared radiation.). This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases. It is believed by many experts to be the primary cause of global warming.Greenhouse gases include substances, such as CO2, nitrous oxide, methane and carbon monoxide.
Greenhouse gases include water vapor, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide (N2O) and other gases. Of particular concern is how climate change and global warming caused by anthropogenic, or human-made releases of greenhouse gases, most notably carbon dioxide, can act interactively, and have adverse effects upon the planet, its natural environment and humans' existence. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced today that it will roll back Obama-era regulations on methane gas, a powerful greenhouse gas.Under the current rules, oil and gas operations are.
A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs infrared (IR) radiation and radiates heat in all directions. A lot of the sun’s energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back into space. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect.
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun. Challenge that is already affecting people and the environment worldwide. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases.
The concentration of climate-heating greenhouse gases has hit a record high, according to a report from the UN’s World Meteorological Organization. Access to these gases is limited by the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer (the Montreal Protocol) and Australian law to help protect the ozone layer and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Of all the various activities leading to greenhouse gas emission, the activities emanating from the industries require special attention.
Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space. In a greenhouse, the sun's heat can come in but cannot go out. Greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on Earth.
Greenhouse effect is being strengthened as human activities (such as the combustion of fossil fuels) add more of these gases to the atmosphere, resulting in a shift in the Earth’s equilibrium. Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth’s average temperature would be about 60º F colder. Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth ’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air.
About 65% of greenhouse warming is. This helps to warm our atmosphere. Thus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewed with concern.
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth’s surface and the air above it. In the 1860s, physicist John Tyndall recognized the Earth's natural greenhouse effect and suggested that slight changes in the atmospheric composition could bring about climatic variations. The problems begin when human activities distort and accelerate the natural process by creating more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere than are necessary to warm the planet to an ideal temperature.
That would make it too cold to support life as we know it. Professor M Mercedes Maroto-Valer and Dr Curtis M. While the greenhouse effect is an essential environmental prerequisite for life on Earth, there really can be too much of a good thing.
These type of gas molecules are. The trapped heat warms the greenhouse. At the United Nations Climate Change Conference held in Paris at the end of last year, 195 countries agreed on a plan to reduce emissions of CO 2 and other greenhouse gases, aiming to limit global temperature increase to well below 2 °C (relative to pre-industrial climate, meaning a future warming of less than 1.4 °C because temperature had.
When sunlight passes through the glass windows of the greenhouse, some of it is reflected by the ground and some is absorbed and later released in the form of. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO. Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer.
In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth’s surface. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect on planets. Carbon dioxide, methane, and other “greenhouse gases” trap heat that would otherwise escape Earth’s atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases occur naturally and are essential to the survival of humans and millions of other living things, by keeping some of the sun’s warmth from reflecting back into space and making. Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid- th century. Greenhouse effect definition, an atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by short-wave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longer-wavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;.
This trapped heat helps in controlle. The greenhouse effect is the increase in global temperatures which result from greenhouse gases trapping solar heat energy in the atmosphere. These gases are nicknamed “greenhouse gases” because of their heat-trapping effect.
With growing concerns about global warming and greenhouse gases (GHG), there is an urgent need to quantify and reduce the environmental impact (EI) of pipeline installation (PI). A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun.
These gases are called greenhouse gases because they act just like a greenhouse — trapping the heat inside the planet’s atmosphere, making the average temperature on Earth 59 degrees Fahrenheit (15 degrees Celsius). Greenhouse gases trap the heat within the Earth's atmosphere. However, as more and more greenhouse gases get into the atmosphere, the Earth will start to grow warmer.
This is because the economy cannot grow without the support of the industrial activities. Certain gases in Earth’s atmosphere—particularly carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and water vapor (H 2)—trap energy from solar radiation and so keep Earth warmer than it would be otherwise.These gases are termed greenhouse gases, and the warming they create is termed the greenhouse effect or greenhouse warming. In the right proportion, these gases do a critical job ensuring the atmosphere holds onto enough heat to support every kind of life on the planet.
The atmospheric gases and a greenhouse work in quite different ways, but the resulting effect, higher temperature in both cases, has led to the nomenclature “greenhouse gases” for the atmospheric gases responsible for the atmospheric warming effect. It is clear the planet is warming, and warming rapidly. The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane.
The gases do this by absorbing the heat and radiating it back to Earth’s surface. Multiple lines of evidence show changes in our weather, oceans, ecosystems, and more. It is named for the effect that keeps greenhouses warm enough to support plants.
The greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now. It is primarily caused by human activities such as the excessive. Some of the heat released reaches the earth, along with heat from the sun that has penetrated the atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that keeps the planet's climate warm enough to support life. Greenhouse gases are not. This phenomenon is called the greenhouse effect and is natural and necessary to support life on Earth.
1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over time. As sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, it passes through the gaseous layer and the Earth's surface absorbs part of the energy and reflects some energy. By increasing the heat in the.
A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere. Although this nomenclature is misleading, it is in such common use that we use it here as well. Greenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun.
Small quantities of ozone depleting substances or synthetic greenhouse gases are required by Australian users for laboratory and analytical uses. Santer et.al., “Contributions of Anthropogenic and Natural Forcing to Recent Tropopause Height Changes,” Science vol. This section provides information on emissions and removals of the main greenhouse gases to and from the atmosphere.
The main greenhouse gases that keep the Earth warm are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane. Greenhouse gas continues to contribute negatively to the environment leading to an uncomfortable society. 78/112 (Energy & Fuels) 40/53 (Engineering, Environmental) 161/265 (Environmental Sciences) Online ISSN.
Climate change is a major risk facing mankind. When it comes to climate and environmental science, the earth is very much like the car, and greenhouse gases are very much like the windows. 19 Journal Citation Reports (Clarivate Analytics):.
Greenhouse gases act like a blanket around Earth, trapping energy in the atmosphere and causing it to warm. Greenhouse gases (GHGs) atmospheric gases that absorb IR radiation - Water vapor, ozone, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, halocarbons (chlorofluorocarbons CFCs). Natural causes alone cannot explain all of these changes.
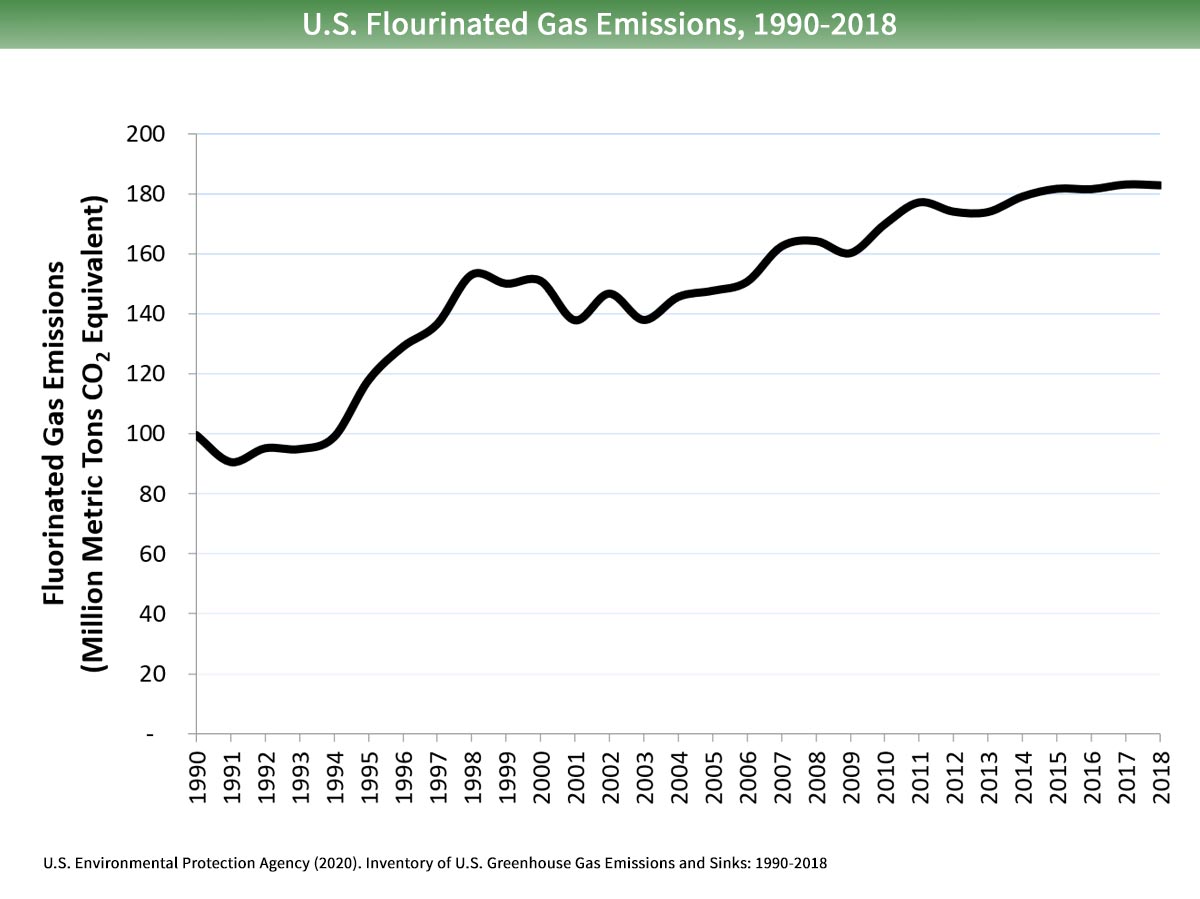
These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Earth's climate is changing. Climate change is a real and urgent.
In the past 100 years humans have been the cause of a significant increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, especially carbon dioxide. The greenhouse gas effect (Source IPCC 07) The increased emissions to the atmosphere of greenhouse gases mean that current levels of gases far exceed their natural ranges. Larger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases.
Gases that absorb radiated heat from the sun, thereby increasing the temperature of the atmosphere. Greenhouse gas Any of the atmospheric gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation produced by solar warming of the Earth's surface. Without the “greenhouse effect,” Earth would be too cold to support most forms of life.
Check out our video on "Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming” by Letstute. Global warming is a term given to the rise in temperature of the earth due to the entrapment of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. 301 (25 July 03), 479-4.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases turn like a blanket, gripping Infra-Red radiation and. Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). They include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor.
These gases prevent heat from escaping to space, somewhat like the glass panels of a greenhouse. Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. These reflected rays of energy get trapped between the Earth's surface and the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases. Planet Earth is warm enough to sustain life thanks to gases in the planet’s atmosphere that hold heat. The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth.
A gas that absorbs infrared radiation;. Some gases, when present in the atmosphere, absorb that reflected energy and redirect it back to Earth as heat. Greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere absorb IR from the sun and release it.
The effect of Biot coefficient and elastic. Greenhouse gases and global warming "Gas molecules that absorb thermal infrared radiation, and are in significant enough quantity, can force the climate system. Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and tropospheric ozone are all greenhouse gases.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist. The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth’s atmosphere. Human activities are contributing to climate change, primarily by releasing billions of tons of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other heat-trapping gases, known as greenhouse gases, into the atmosphere every year.
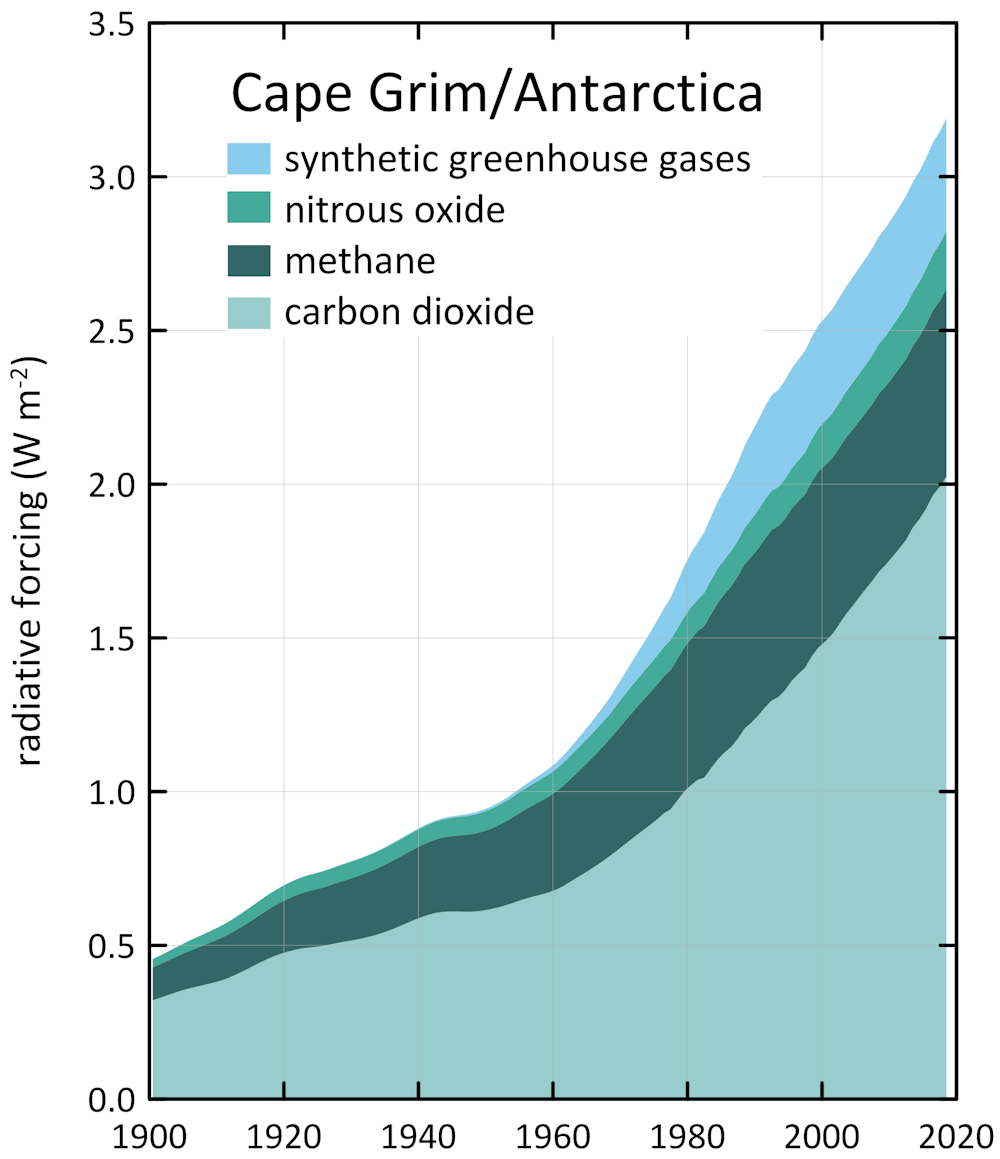
Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Climate Change Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Energy Efficency

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
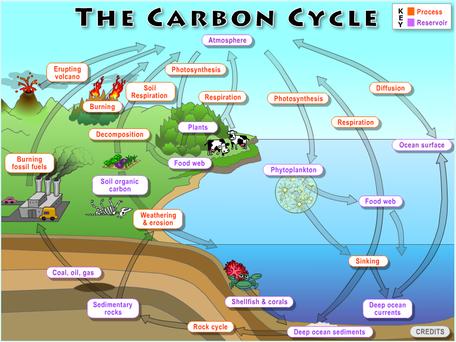
Climate And The Carbon Cycle Unit Overview

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know
3
Sf6 Worries The Most Potent And Persistent Greenhouse Gas Advanced Science News

Climate Myths Carbon Dioxide Isn T The Most Important Greenhouse Gas New Scientist
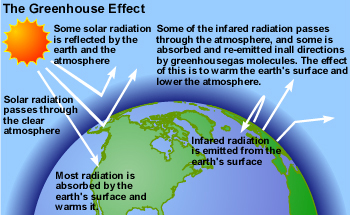
Greenhouse Effect North Carolina Climate Office

Semester One Final

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Of Colleges And Universities Wilkes University

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
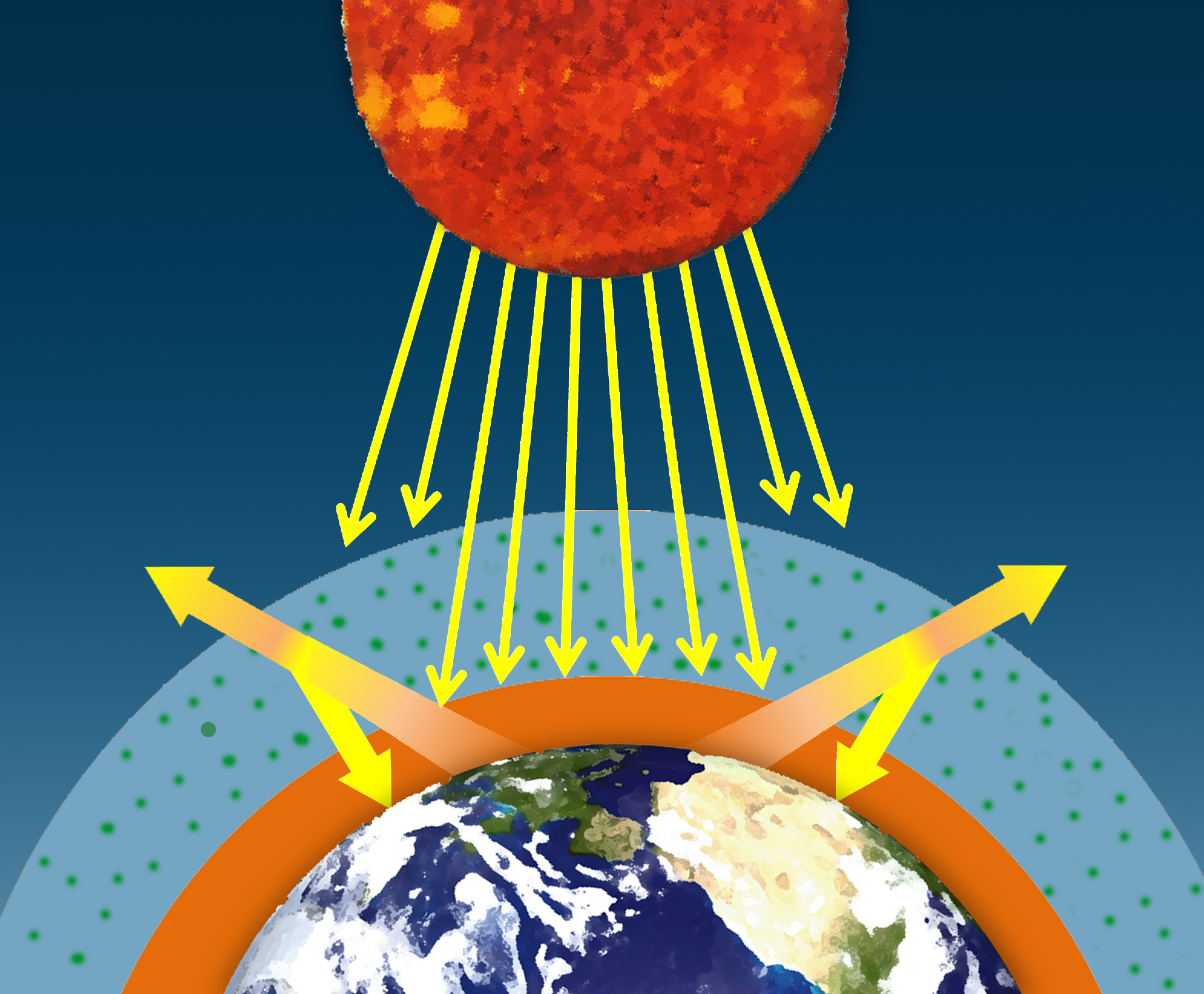
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate

Environmental Impacts Of Food Production Our World In Data

5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Canada Ca

Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa

Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming

Food Waste Is Responsible For 6 Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data

The Warming Effect Is Valuable To All Life On Earth Except Maybe Some Microbes Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse

History Of The Study Of Climate Change In Field Of Environmental Science Environmentalscience Org

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change

What Is Global Warming Live Science

Greenhouse Effect Dictionary Definition Greenhouse Effect Defined
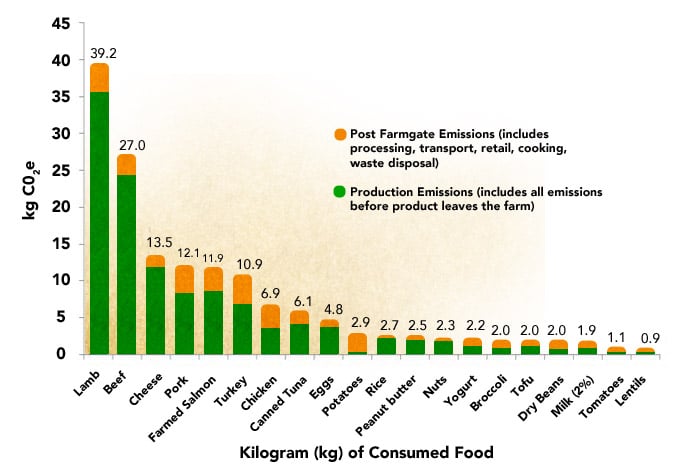
The Impacts 11 Meat Eaters Guide Meat Eater S Guide To Climate Change Health Environmental Working Group

What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
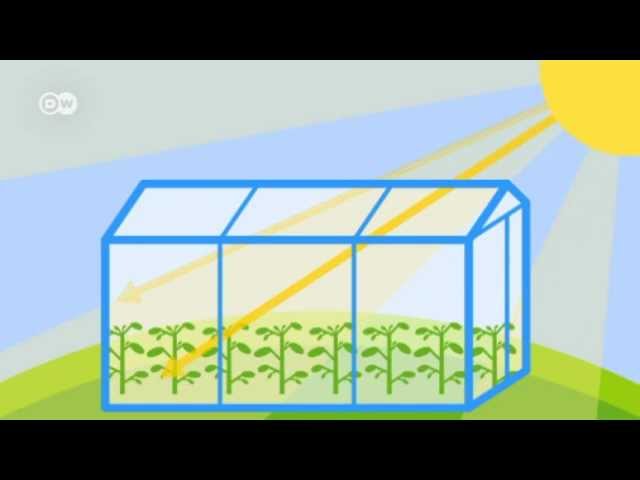
What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Ideas Youtube

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science
Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrvmdulfatosq84aycswgwbxtspixdct1mgyrvhn7klldjmlkws Usqp Cau

Environmental Science Chapter 13 Review Chlorofluorocarbons Compounds That Contain Chlorine Cause Ozone Destruction In Upper Atm Climate Described Ppt Download

Pin By Sophia On Enviornmental Sciences Project Environmental Science Projects Greenhouse Gases Science Projects

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
Climate Change Mitigation Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsrkshs4yxsmfkaj 7o4ctqd2sjucsgee2fpvlscwmrhqroqc Usqp Cau

Climate Change Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Energy Efficency

An Essay On Global Warming Causes And Its Effects With Images Global Warming Facts Global Warming Climate Change Global Warming

Efficiency Gap Analysis For Strong Sustainability Using Greenhouse Gas Download Scientific Diagram
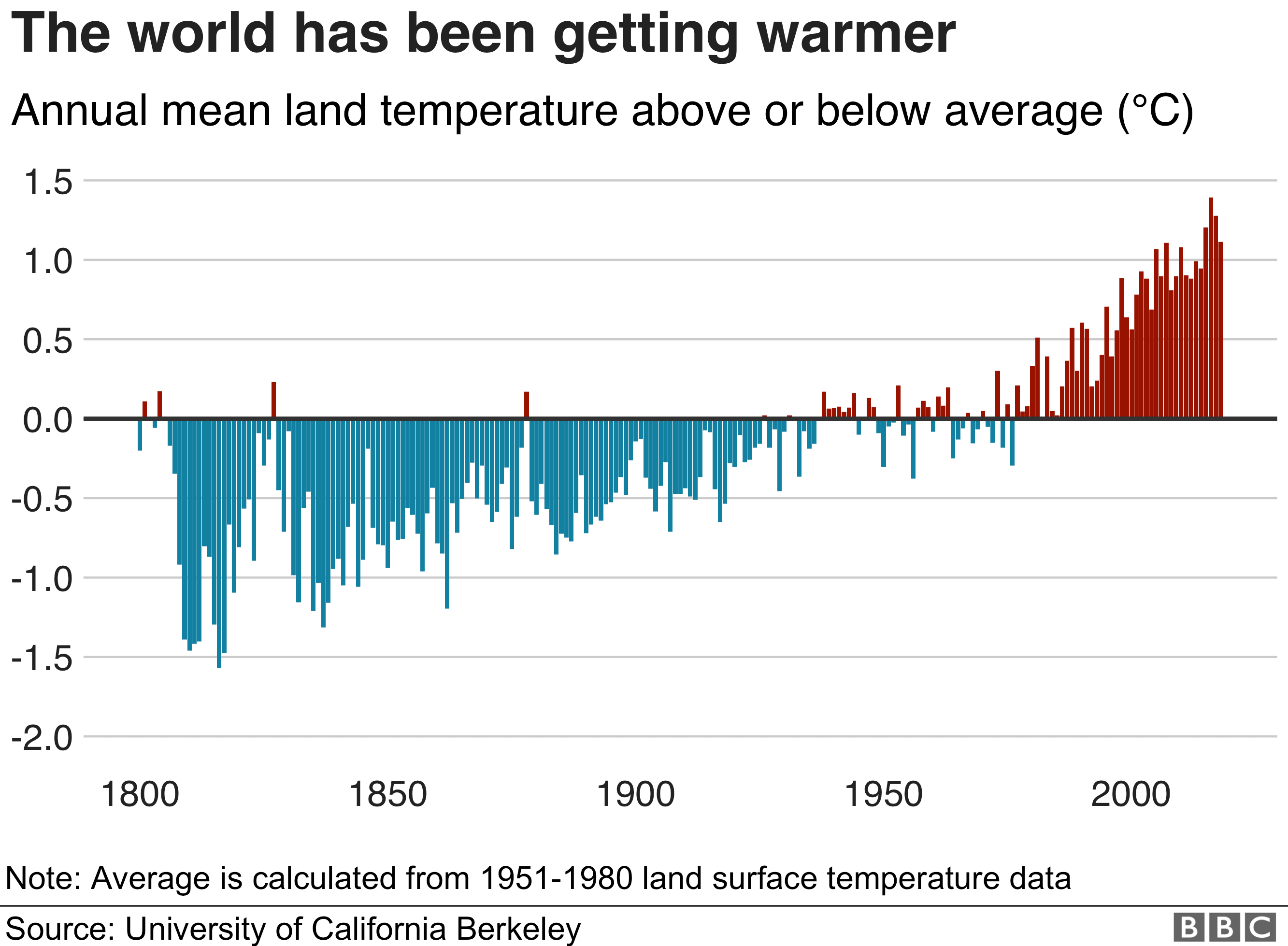
What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News

Solved Im Doing Environmental Science Questions But Im No Chegg Com
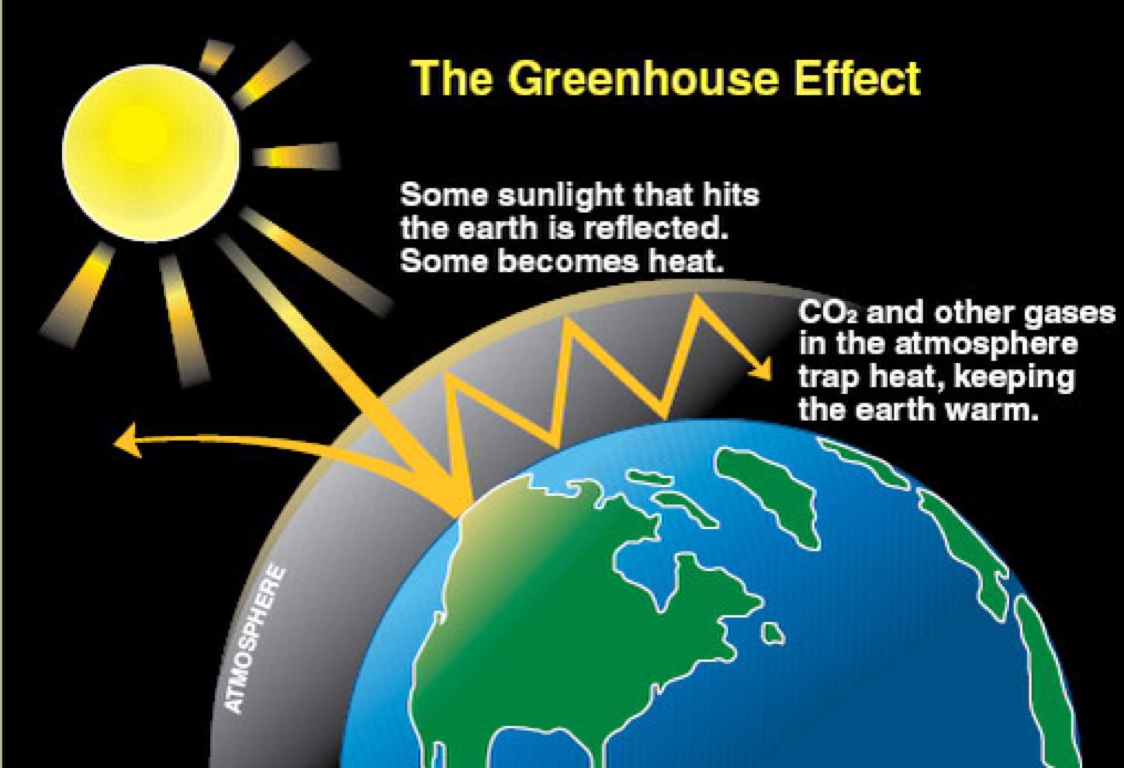
What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic

Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute

Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences

Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
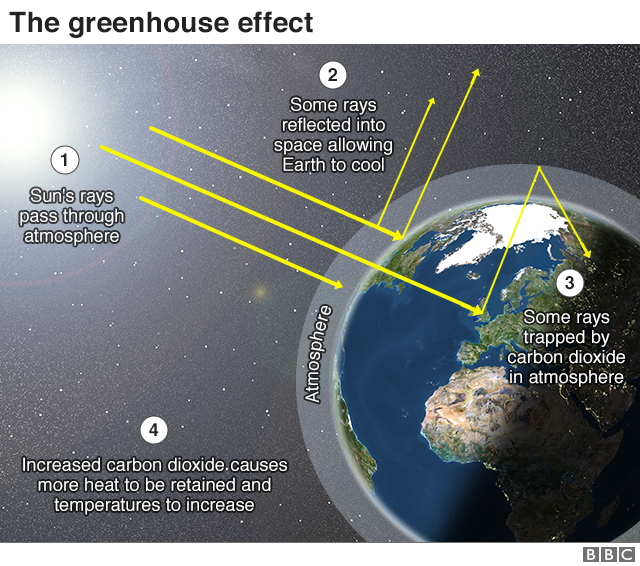
What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
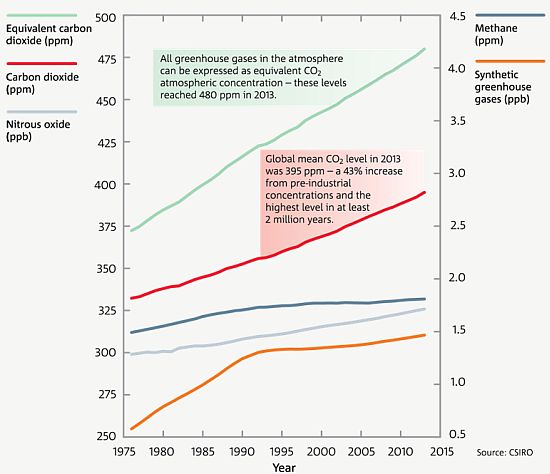
Greenhouse Gases

The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education
Environment For Kids Global Warming

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
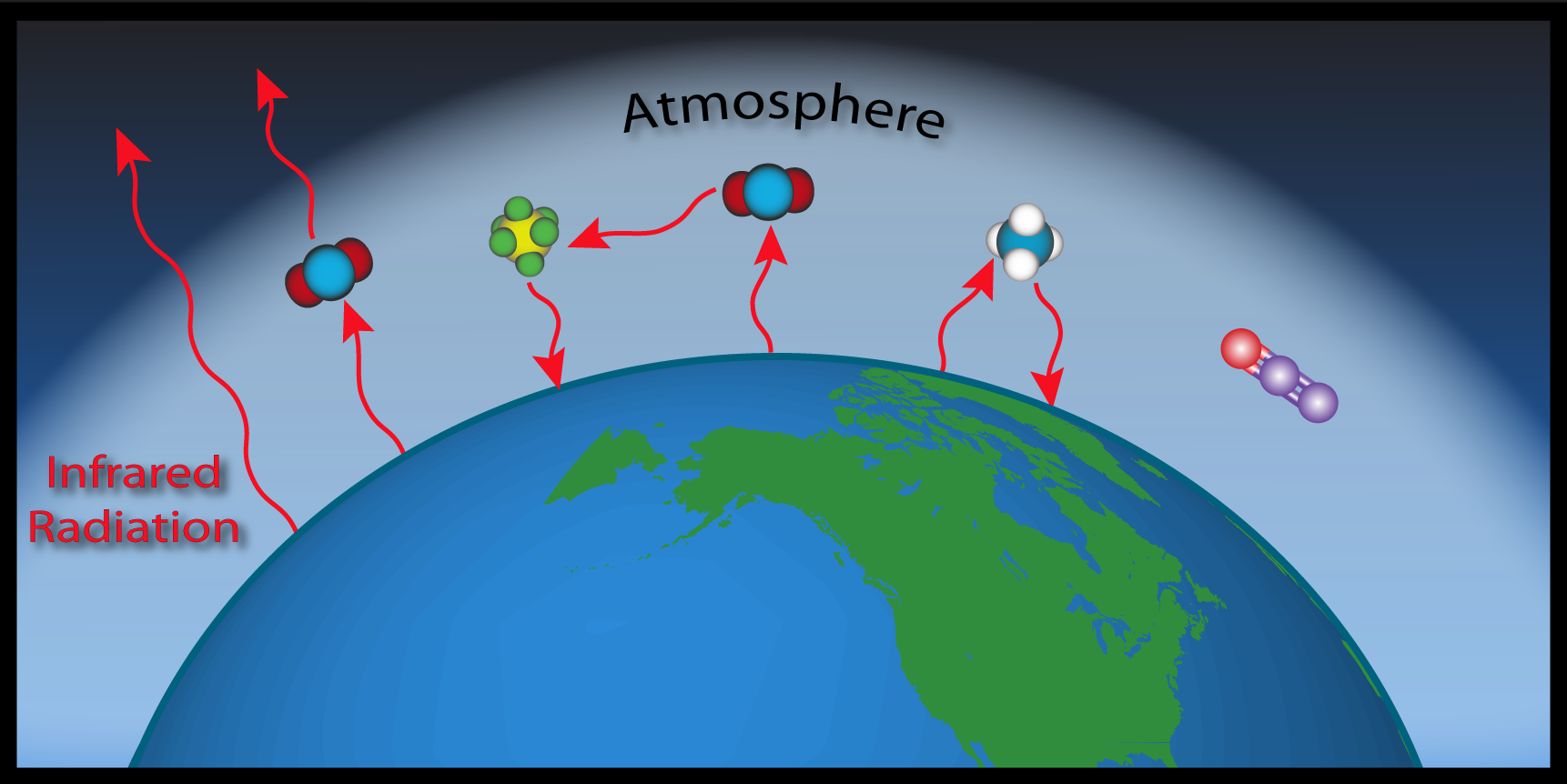
What Is The Greenhouse Effect And How Does It Affect Our Life

Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
1

Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
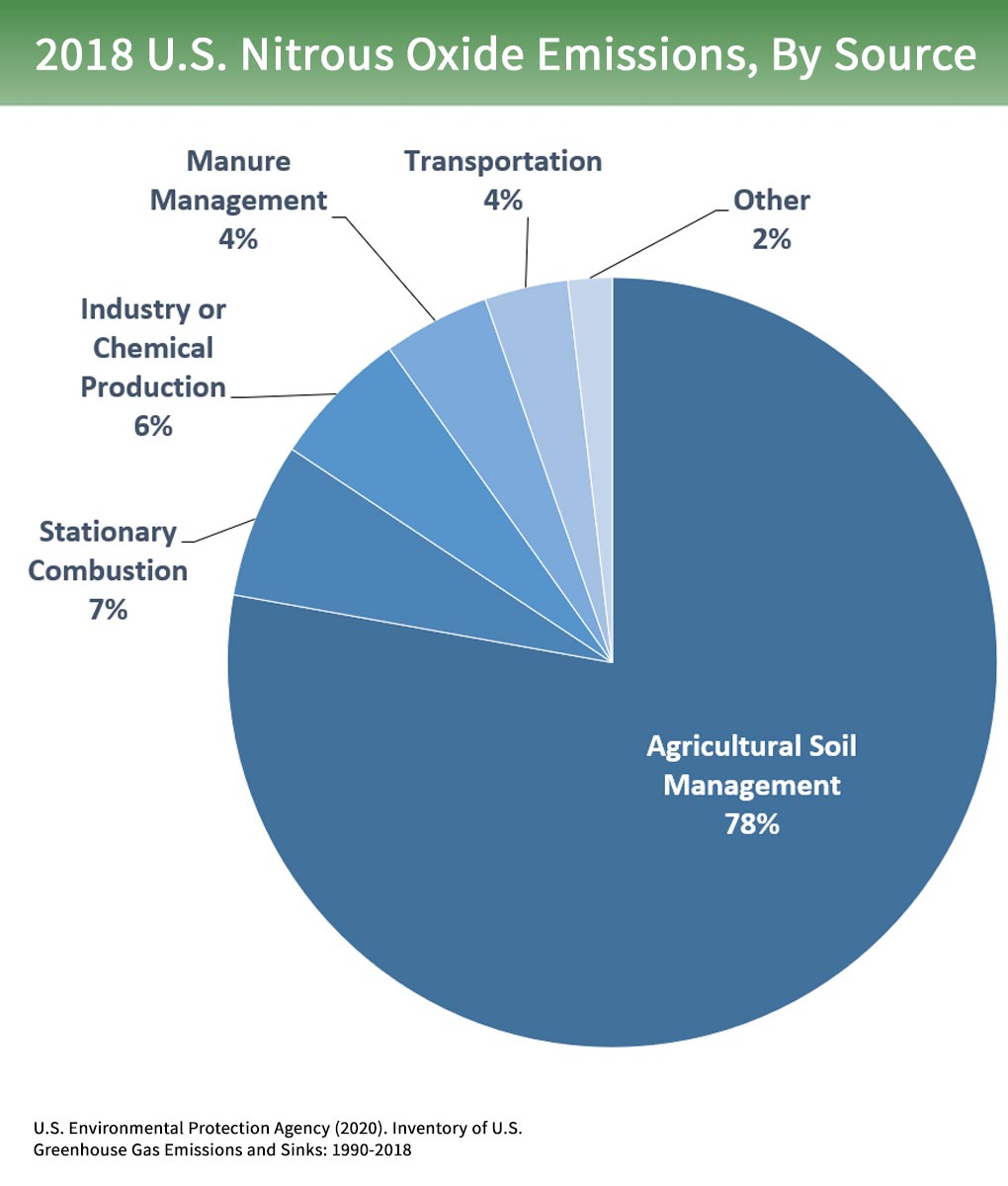
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation

Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
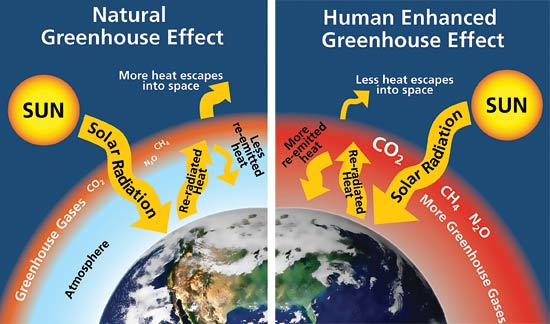
How Is The Greenhouse Effect Related To Global Warming Socratic
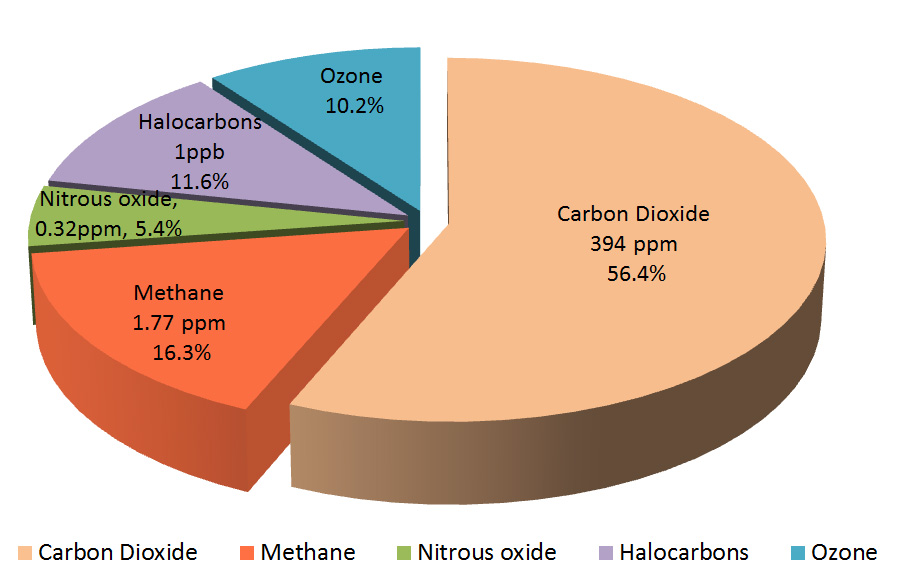
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions

Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
Climate Change And Agriculture Wikipedia

Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Causes Of The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future

Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia

Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts

Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
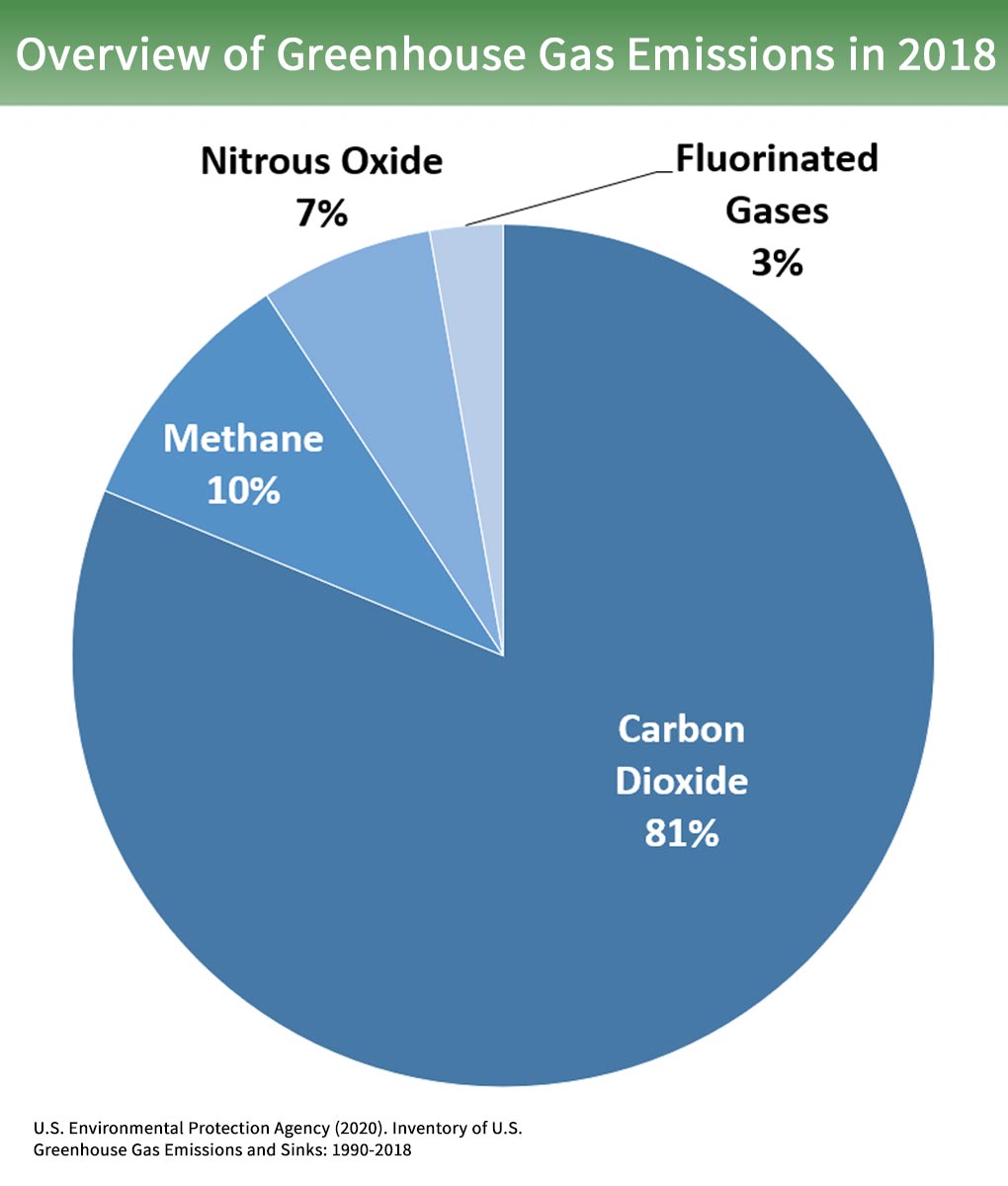
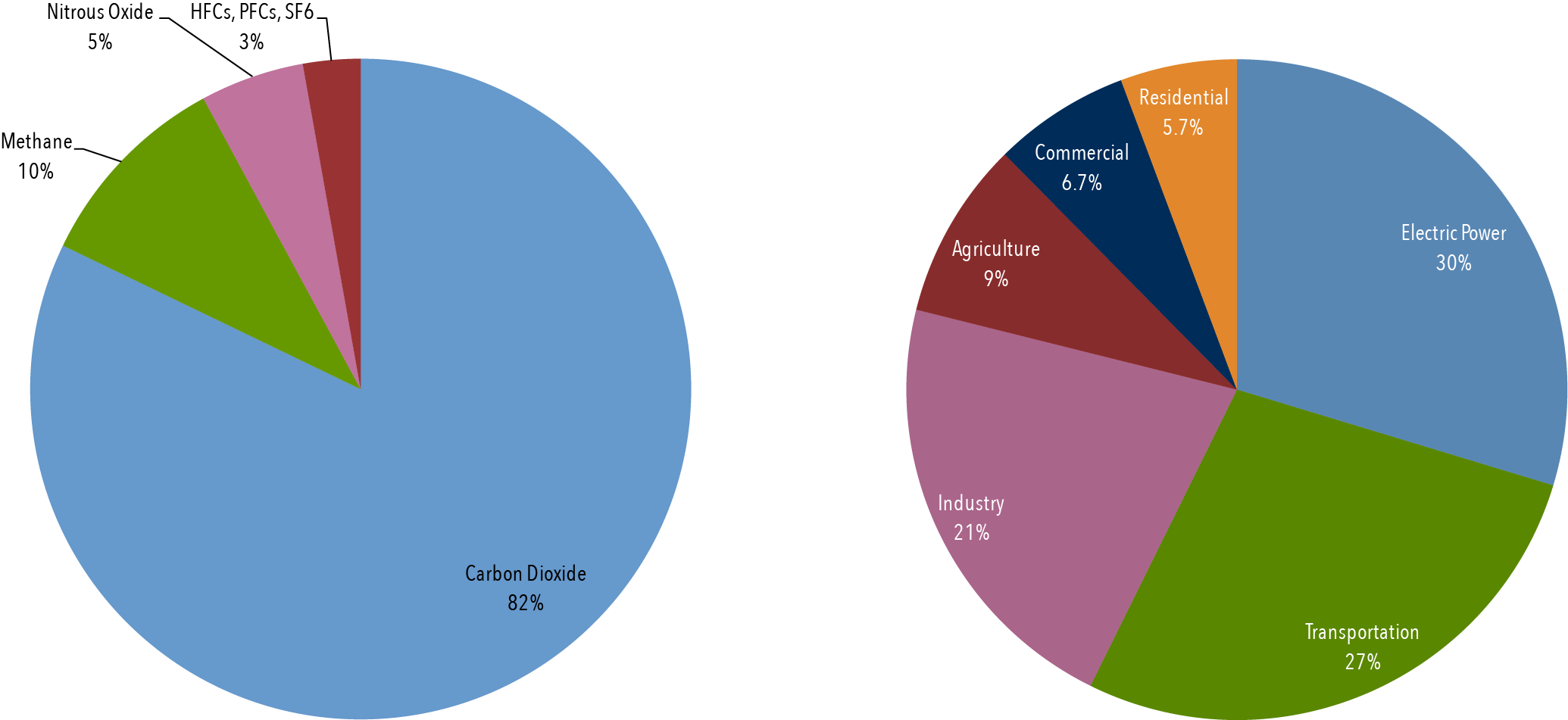
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
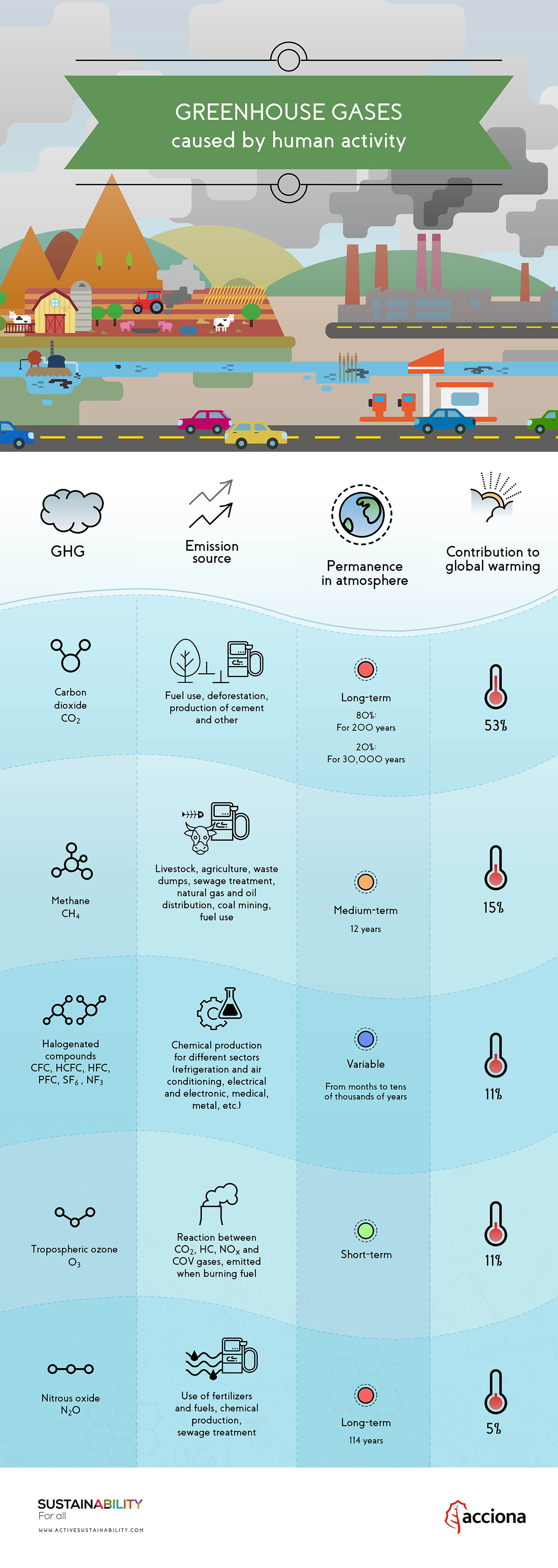
How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming
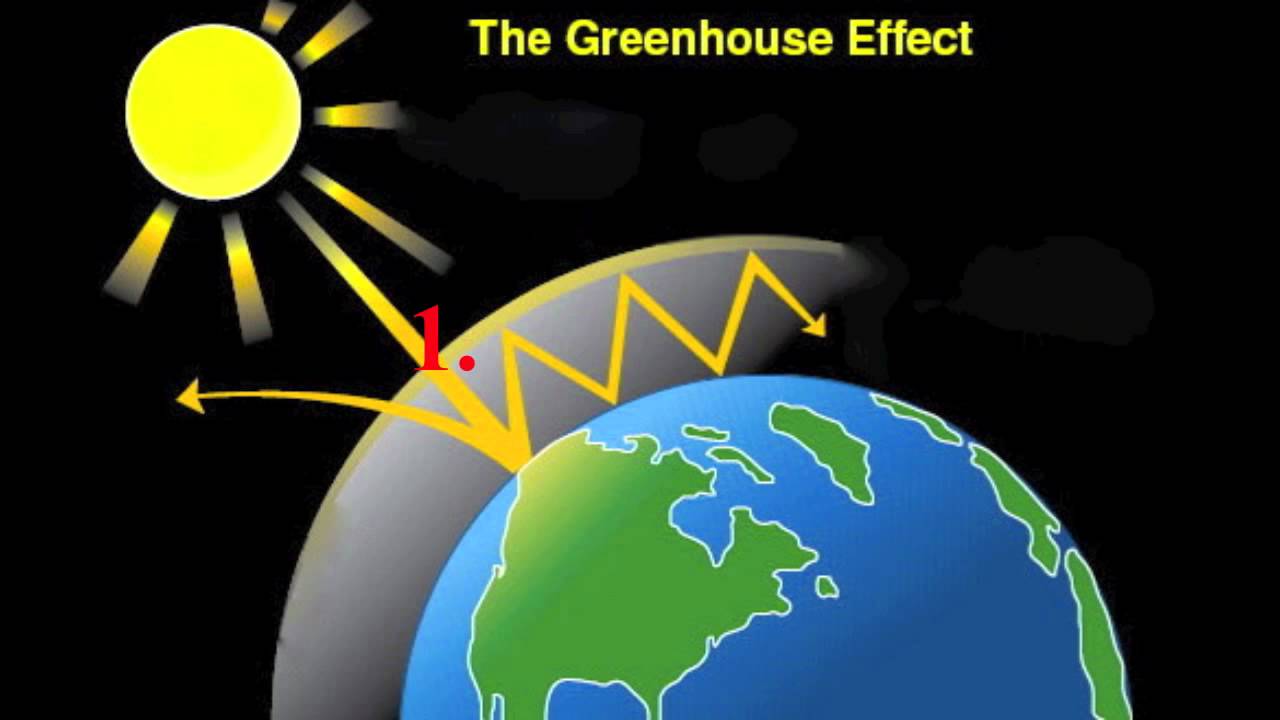
Greenhouse Effect For Kids

What Is Nitrous Oxide And Why Is It A Climate Threat Insideclimate News

Explaining The Greenhouse Effect Sustainability Youtube
Http Www Campbellcountyschools Org Userfiles 1591 Greenhouse effect global warming lab Pdf

The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef

What Are The Main Man Made Greenhouse Gases Environment The Guardian

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious

Advantages Or Disadvantages Of The Greenhouse Effect By Maria Mith Medium

Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
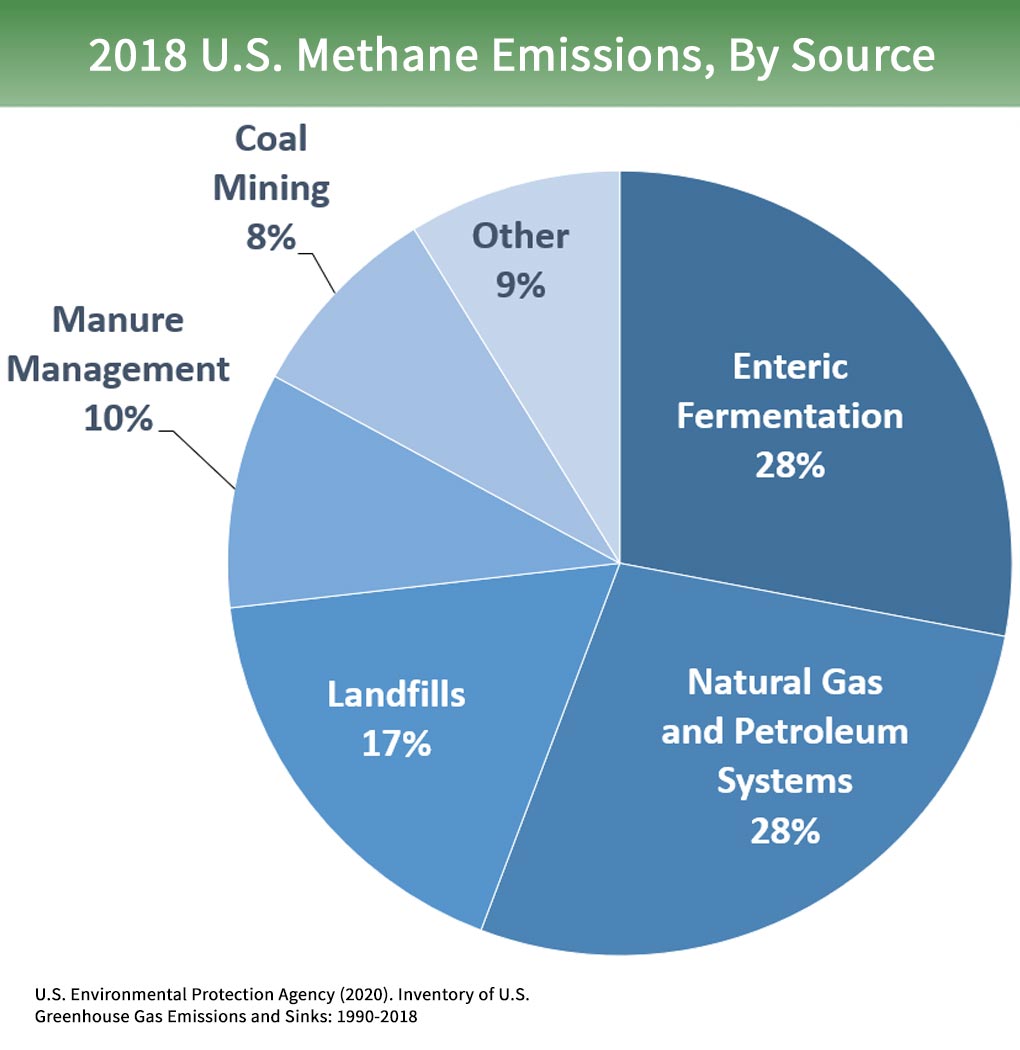
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Causes Sources Live Science

Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students

Climate Change Lecture Outline

What Is The Greenhouse Effect Howstuffworks

Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society

Environmental Science Rocks Global Warming Project Global Warming Global Warming Poster

Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia

Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute



