Greenhouse Gasses
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming
New Land Use Strategies Can Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa
Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming

How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut

New Hampshire Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Climate Change Program Nh Department Of Environmental Services
Trust our experts with your next greenhouse project.

Greenhouse gasses. Some, such as industrial gases, are exclusively human made. Greenhouse gases absorb reflected solar energy, making the Earth's atmosphere warmer. The greenhouse effect is the rise in temperature that the Earth experiences because greenhouse gases trap energy from the sun.
Coronavirus Live Updates Global energy demand, particularly for coal, is falling sharply this year, the. Some gases occur naturally and are also produced by human activities. Greenhouse gases absorb this infrared radiation and trap its heat in the atmosphere, creating a greenhouse effect that results in global warming and climate change.
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth’s atmosphere. This final rule "tailors" the requirements of these Clean Air Act permitting programs to limit which facilities will be. Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat.
By increasing the heat in the. A greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. The atmosphere is largely transparent to the Sun’s energy, most of which arrives in the form of light.
And while a few. That means that the majority of warming. When people burn fossil fuels such as coal, gasoline, oil and natural gas, there is an increased level of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere, which is a major contributor to global warming and greenhouse effect.The emissions basically trap heat close to the surface of the earth.
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gases. These emissions trap heat close to the earth, causing what is known as the. Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight.
Greenhouse gasses include water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide. These heat-trapping gases are called greenhouse gases. Now, over a century later, the mention of greenhouse gas usually evokes thoughts of carbon dioxide (CO 2).That’s mainly because changes in the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere have been linked to the warming of the atmosphere over this past century.
As these geologic formations release carbon dioxide, plants rely on it to perform photosynthesis which results in oxygen production. However, Earth’s greenhouse effect is getting stronger as we add greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth.
An introduction to the major greenhouse gases in the earth's atmosphere. One of the most well-known impacts of climate change is rising temperatures. CO 2 is an important greenhouse gas, and along with water vapor, keeps the Earth warm enough to support life as we know it.
Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6). Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth ’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution ., coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips.
Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3).Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth. The Worldwatch Institute included agriculture’s supply chain as well, and it concluded that livestock agriculture is responsible for 51 percent of anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions.
Monitoring of GHG data began in 10 for most sources. Water vapor accounts for by far the largest greenhouse effect (90–85%) because water. Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of industrial processes.
Without the greenhouse effect, Earth’s temperature would be below freezing. That's because we produce more carbon dioxide than any other greenhouse gas, and it's responsible for most of the warming. The primary greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone.
Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas, responsible for about three-quarters of emissions. Once absorbed, this energy is sent back into the atmosphere. The Earth's surface absorb the sunlight’s energy.
Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3). During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere. The EPA Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program collects greenhouse gas data from large emission sources (facilities that emit 25,000 metric tons of GHGs or more per year), as well as suppliers of products that could emit greenhouse gases.
Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat just like the glass roof of a greenhouse. Human emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world’s most pressing challenges. Greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on Earth.
Greenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbons. Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth’s temperature over geologic time. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that define when permits under the New Source Review Prevention of Significant Deterioration (PSD) and Title V Operating Permit programs are required for new and existing industrial facilities.
Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of the make-up of our atmosphere.
These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Atlas Manufacturing offers a full line of quality commercial, educational, and hobby greenhouses and all the accessories to go with it at affordable prices. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Predicted To Fall Nearly 8% — Largest Decrease Ever :.
That sunlight creates warmth. The danger lies in the rapid increase of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that intensify this natural greenhouse effect. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect.
If people are to reduce the greenhouse effect, then they have. Carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas you hear people talk about the most. Radiatively active gases (i.e., greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions.Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, warming it.
Greenhouse gases are a group of compounds that are able to trap heat (longwave radiation) in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth's surface warmer than it would be if they were not present. 25 Wonderful Ways to Reduce Greenhouse Gases. Call us at 800.346.9902!.
Sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, passing through the blanket of greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect on planets. These molecules are able to absorb heat, which makes them vibrate.
Too much greenhouse effect:. A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere. There may not be much of some of these gasses in our atmosphere, but they can have a big impact.
Perhaps the most well-known global greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide. 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth’s history. As humans burn more and more fossil fuels, carbon dioxide (and other greenhouse gases) trap more and more heat in our atmosphere.
Without naturally-occurring, heat-trapping gases—mainly water vapour, carbon dioxide and methane—Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it. As you probably know, carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) and other greenhouse gases act like a blanket, absorbing IR radiation and preventing it from escaping into outer space. Earth is sometimes called the “Goldilocks” planet – it’s not too hot, not too cold, and the conditions are just right to allow life, including us, to flourish. They get their name from greenhouses.
A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight. The Venus greenhouse effect shows you what happens when this the process of trapping sunlight goes out of control into a runaway process. Life on Earth depends on the presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere to insulate our planet’s surface against the chill of space;.
Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%). The heat caused by infrared radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gasessuch as water vapor, carbon dioxide, ozone, and methane, which slows its escape from the atmosphere. The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth’s atmosphere.
Some gases, when present in the atmosphere, absorb that reflected energy and redirect it back to Earth as heat. Despite all the talk about carbon capture, carbon footprints and carbon trading, carbon dioxide only causes nine to 26 percent of the greenhouse effect. Many gases exhibit these greenhouse properties.
2 Increases in the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere enhances the greenhouse effect which is creating global warming and consequently climate change. 1 The largest source of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities in the United States is from burning fossil fuels for electricity, heat, and transportation. It is, in part, a natural process.
The atmosphere of Venus, like Mars, is nearly all carbon dioxide. Without them the Earth’s average climate would be about 33 °C cooler. Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1-270 years for HFCs to 800-50,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6.
The net effect is the gradual heating of Earth's. Carbon dioxide is the most important greenhouse gas emitted by humans, but several other gases contribute to climate change, too. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides.
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth’s surface and reradiating it back to Earth’s surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect. A lot of the sun’s energy reaches the ground directly, and a portion is reflected by the ground back into space. It occurs naturally in volcanoes, hot springs, groundwater, and glaciers.
Human activities are responsible for almost all of the increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere over the last 150 years. The FAQ discusses the relative potency, concentration and expected atmopsheric lifetime. Each greenhouse gas molecule is made of three or more atoms that are bonded loosely together.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO 2) is a nontoxic, colorless, odorless gas. Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents, refrigerants. Between 1980 and 15, the average temperature in Atlanta has risen nearly 2 degrees Fahrenheit (1.11 degrees Celsius).
It can linger in the atmosphere for thousands of years. But Venus has about 154,000 times as much carbon dioxide in its atmosphere as Earth (and about 19,000 times as much as Mars does), producing a runaway greenhouse effect and a surface temperature hot enough to melt lead. A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs and emits infrared radiation.
2 To set the scene, let’s look at how the planet has warmed. 1 These gases are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect.
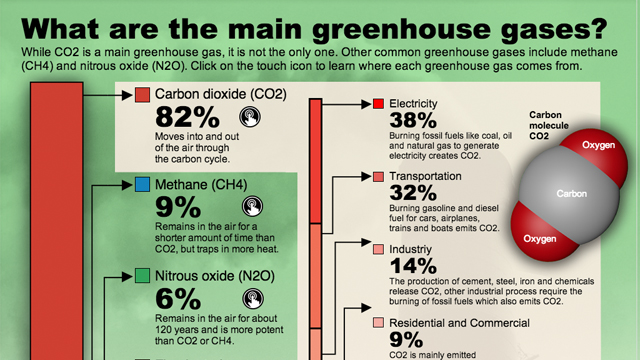
What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed
Atmo336 Spring

Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Nys Dept Of Environmental Conservation
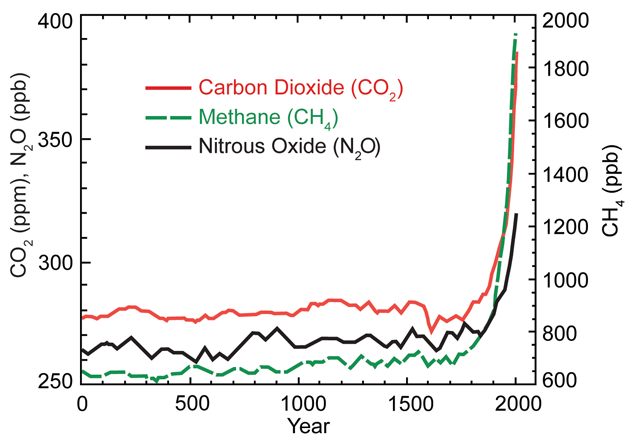
00 Years Of Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Global Climate Change Impacts In The United States 09 Report Legacy Site

What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation

How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)
Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy
Q Tbn 3aand9gctujnkpe1mz4qzgyq38lulzrbobyehd9fhwgqq0it06njqwsl Usqp Cau

Ecoistic Greenhouse Gas Blues Fighting The Emission War

How Are Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases By The Eu Evolving

Trends In Global Co2 And Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 18 Report Pbl Planbureau Voor De Leefomgeving

Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa

The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters

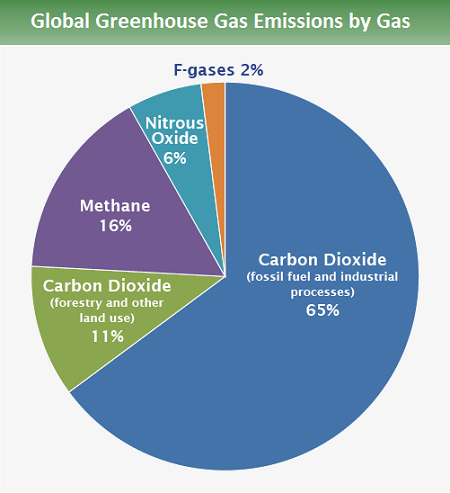
Slicing The Greenhouse Gas Pie What Gases
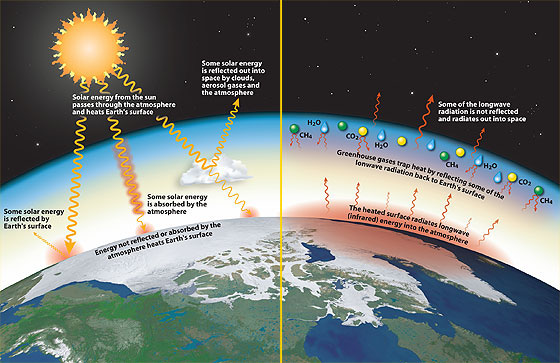
Too Much Of A Good Thing

Eskom Sasol Emit Over Half Of South Africa S Greenhouse Gas

Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
1

Greenhouse Gases World Meteorological Organization

Climate Change International Ccs Knowledge Centre

The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education
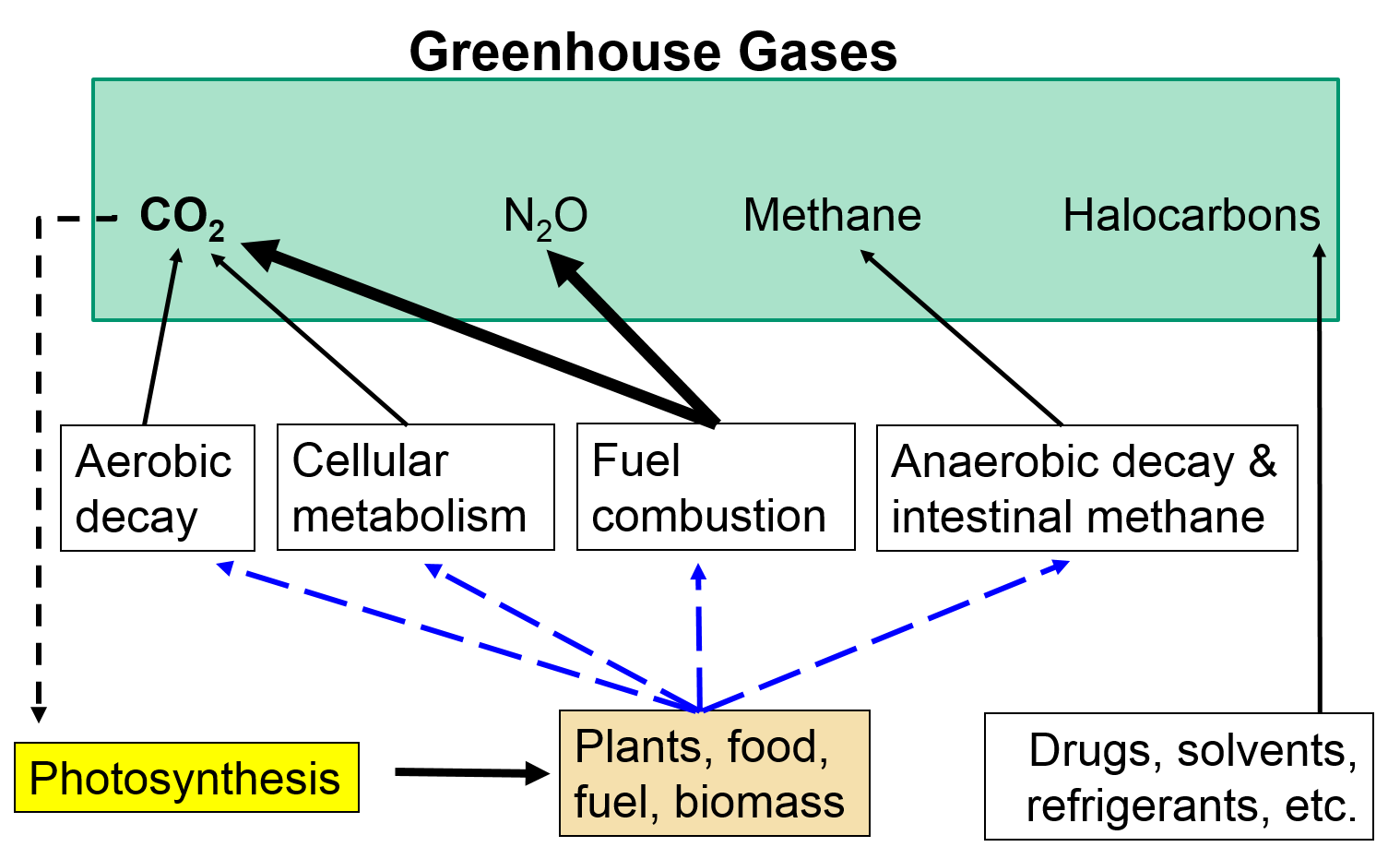
Greenhouse Gases Climate Change

Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From
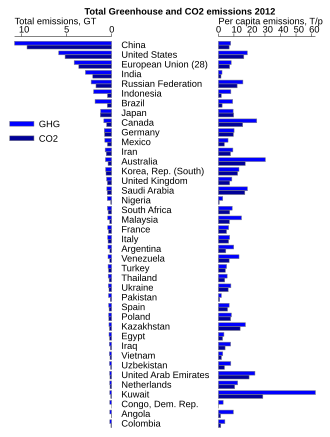
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

Dnr Reports 3 Increase In Iowa Greenhouse Gas Emissions Iowa Environmental Focus

Climate Change Actual Report Greenhouse Gas Emissions Need For Changing
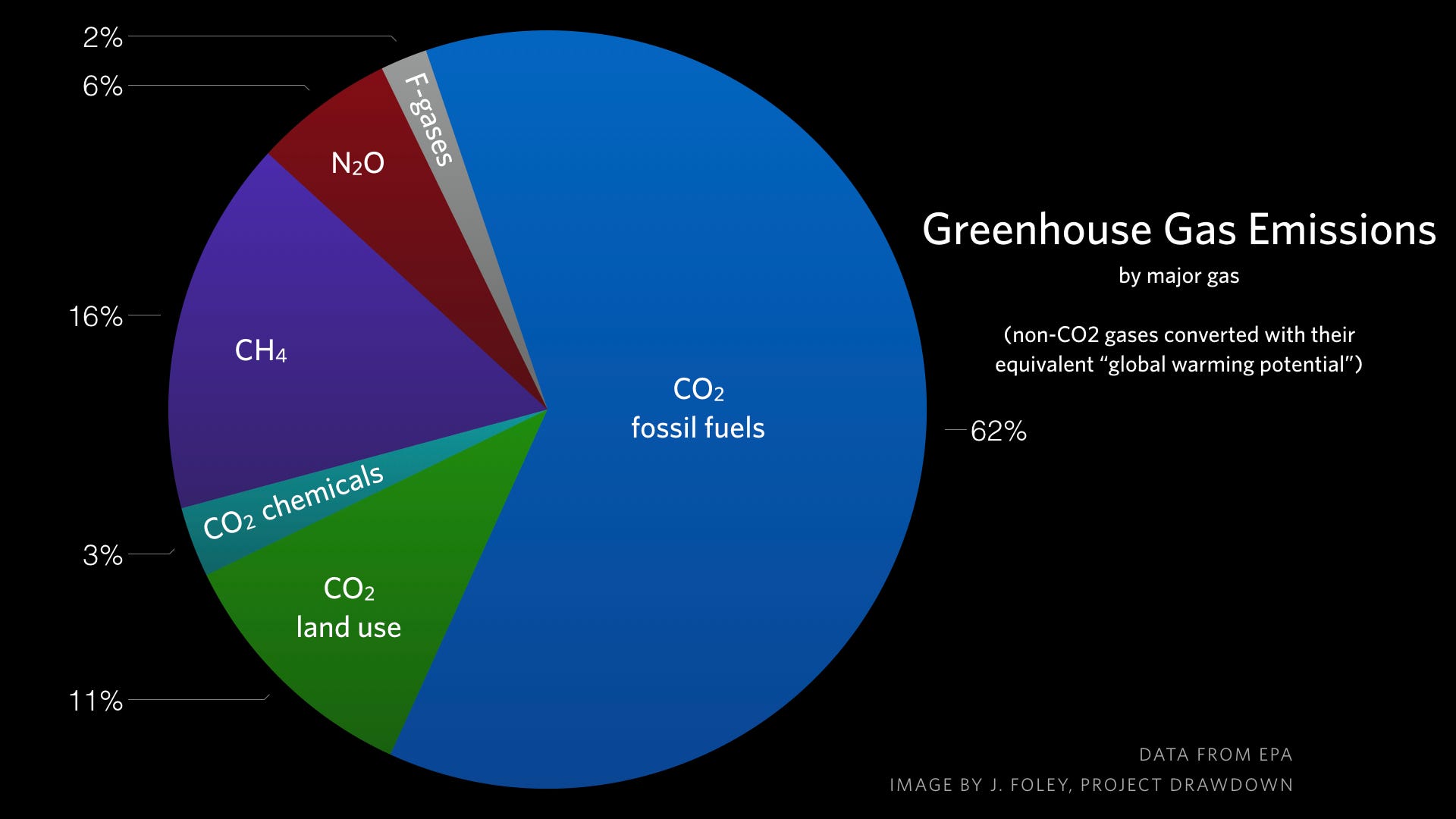
Major Causes Of Climate Change Dr Jonathan Foley
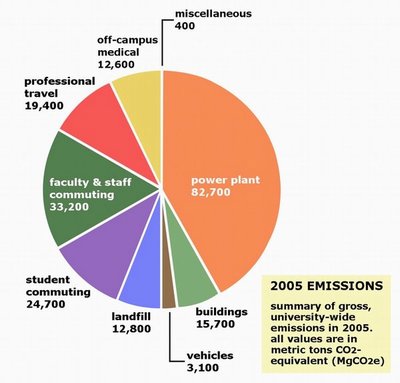
Uw Greenhouse Gases Down 10 Percent From 01 To 05 Inventory Finds Uw News
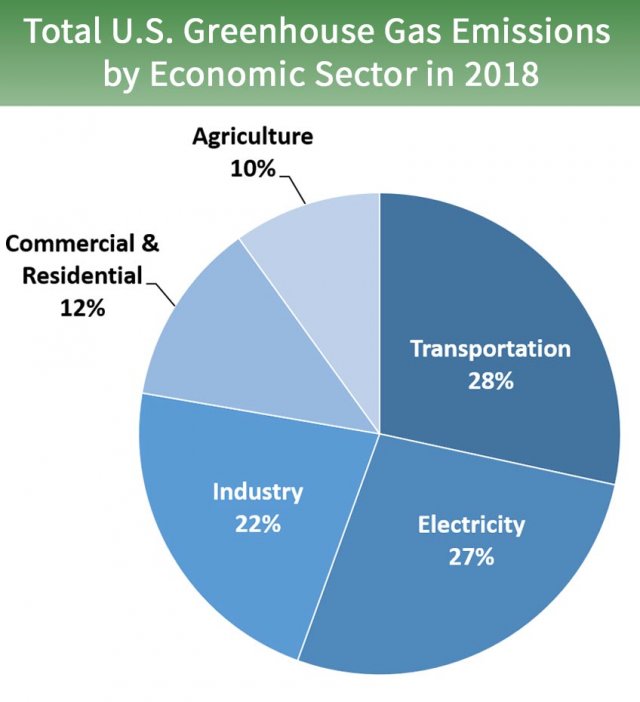
Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
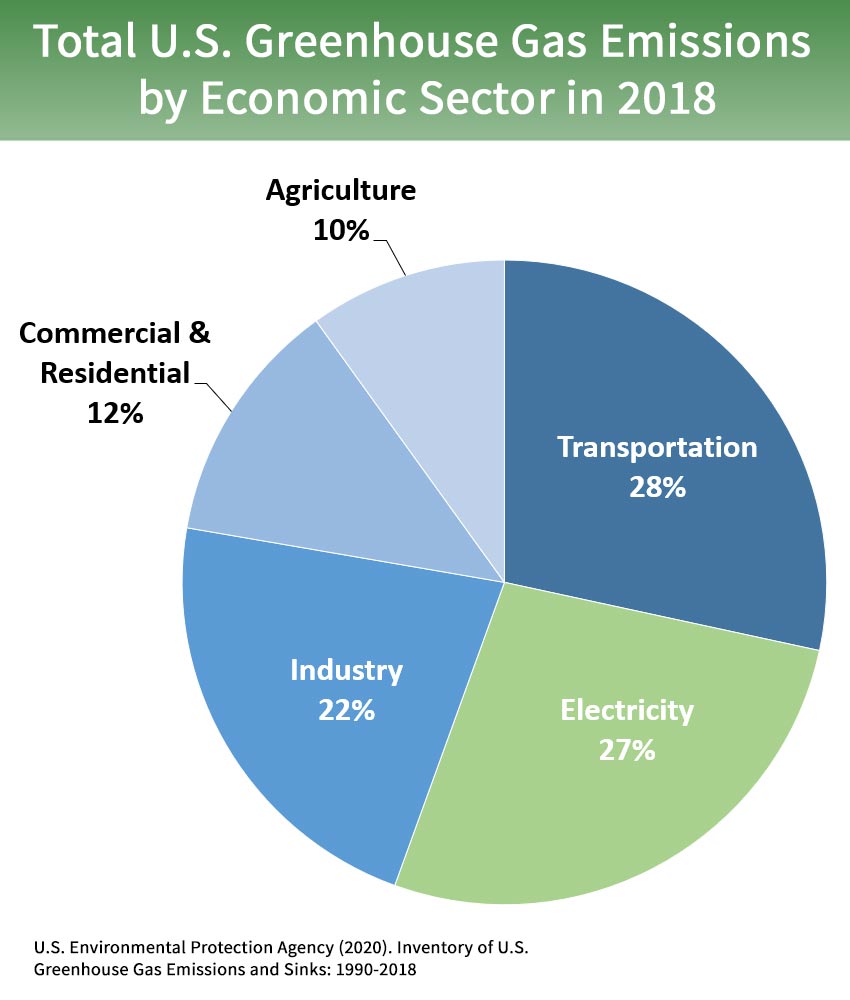
Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrghuhjof8kgcyakufa Ffhrtgwqhmmjleaq0ppauamq1v32qhd Usqp Cau
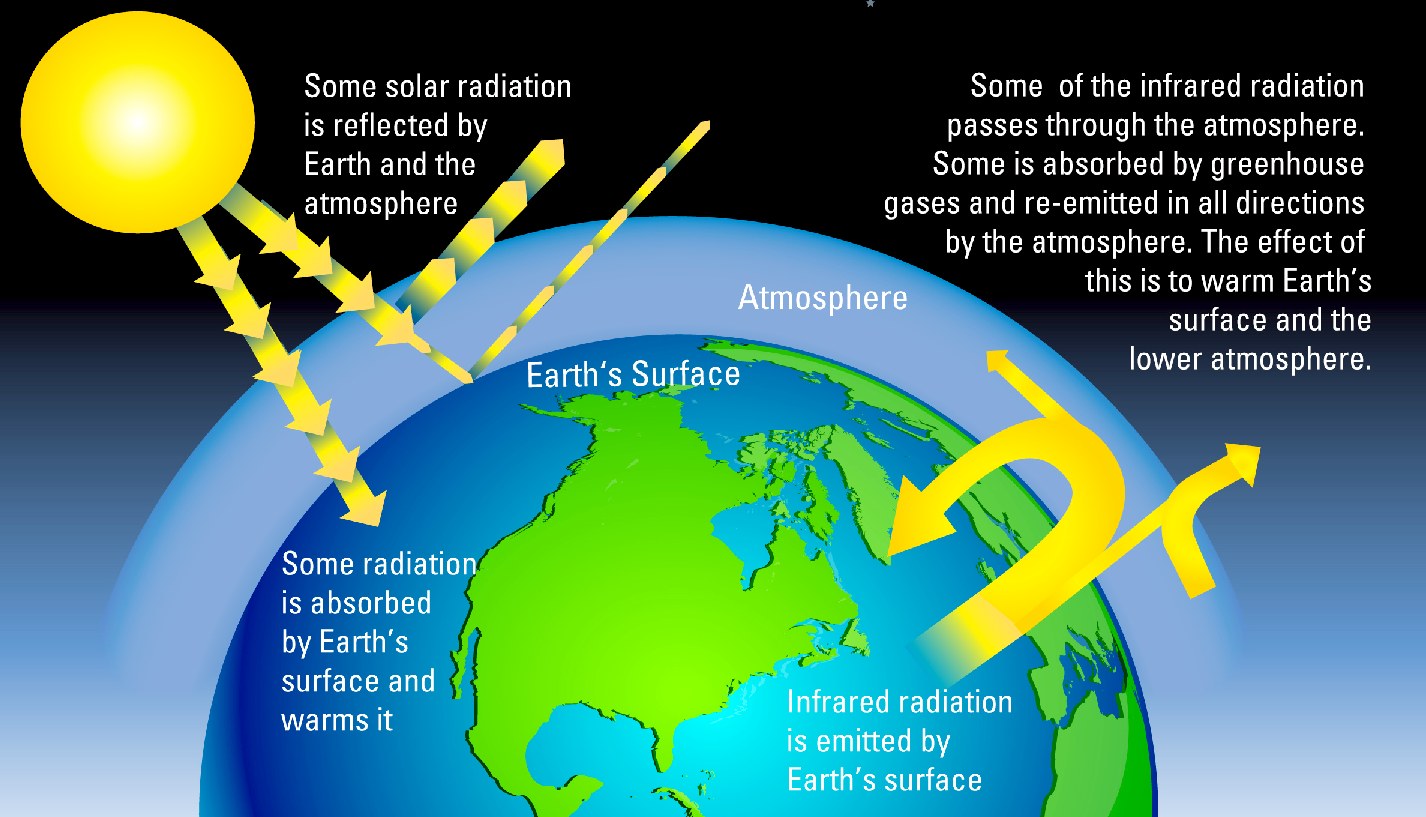
Greenhouse Gases

China And U S Are Biggest Emitters Of Greenhouse Gases Worldwide

Un Greenhouse Gasses Reach Record High Voice Of America English
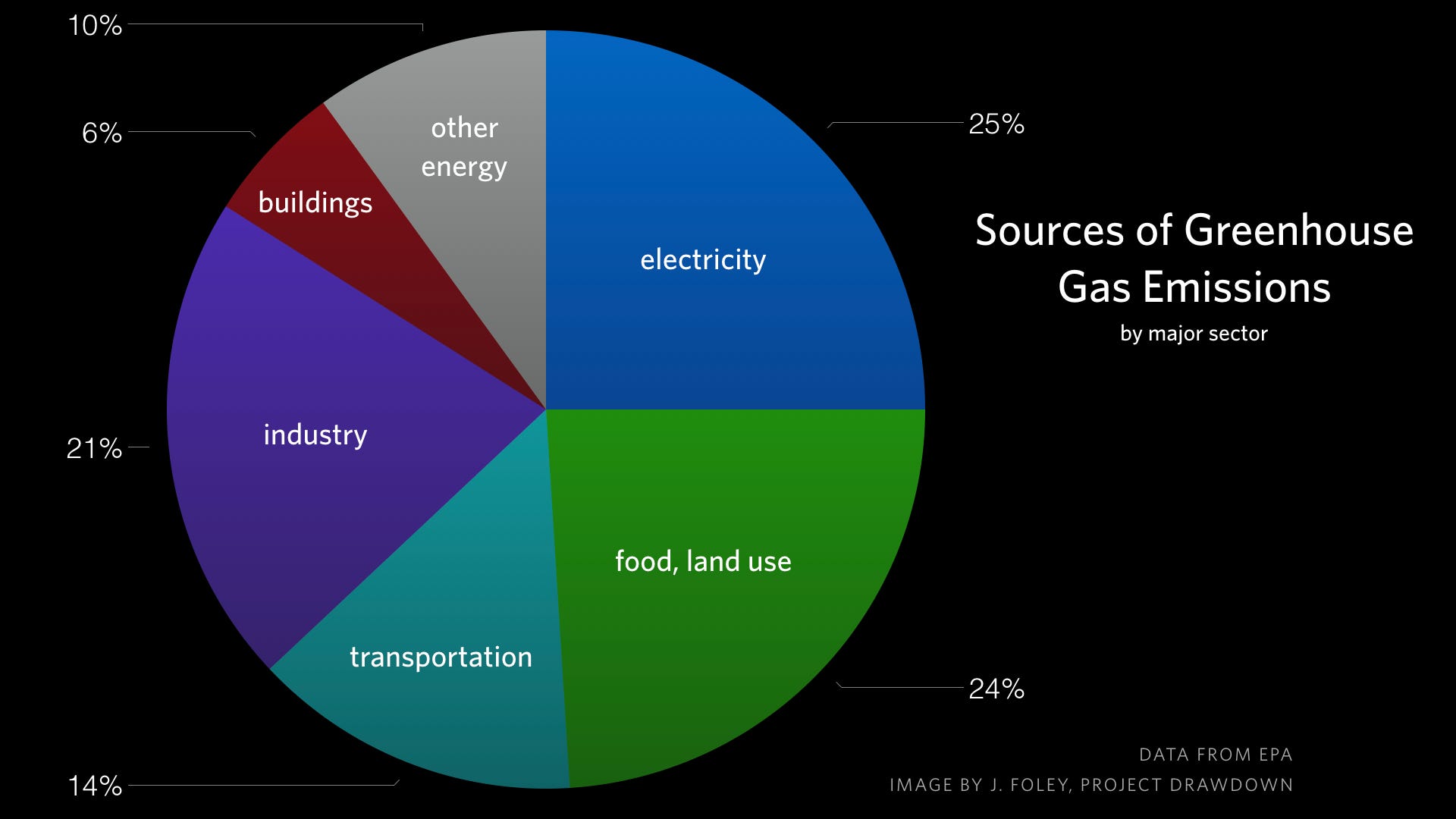
Major Causes Of Climate Change Dr Jonathan Foley

Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S

Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia

These Are The Causes Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Greenhouse
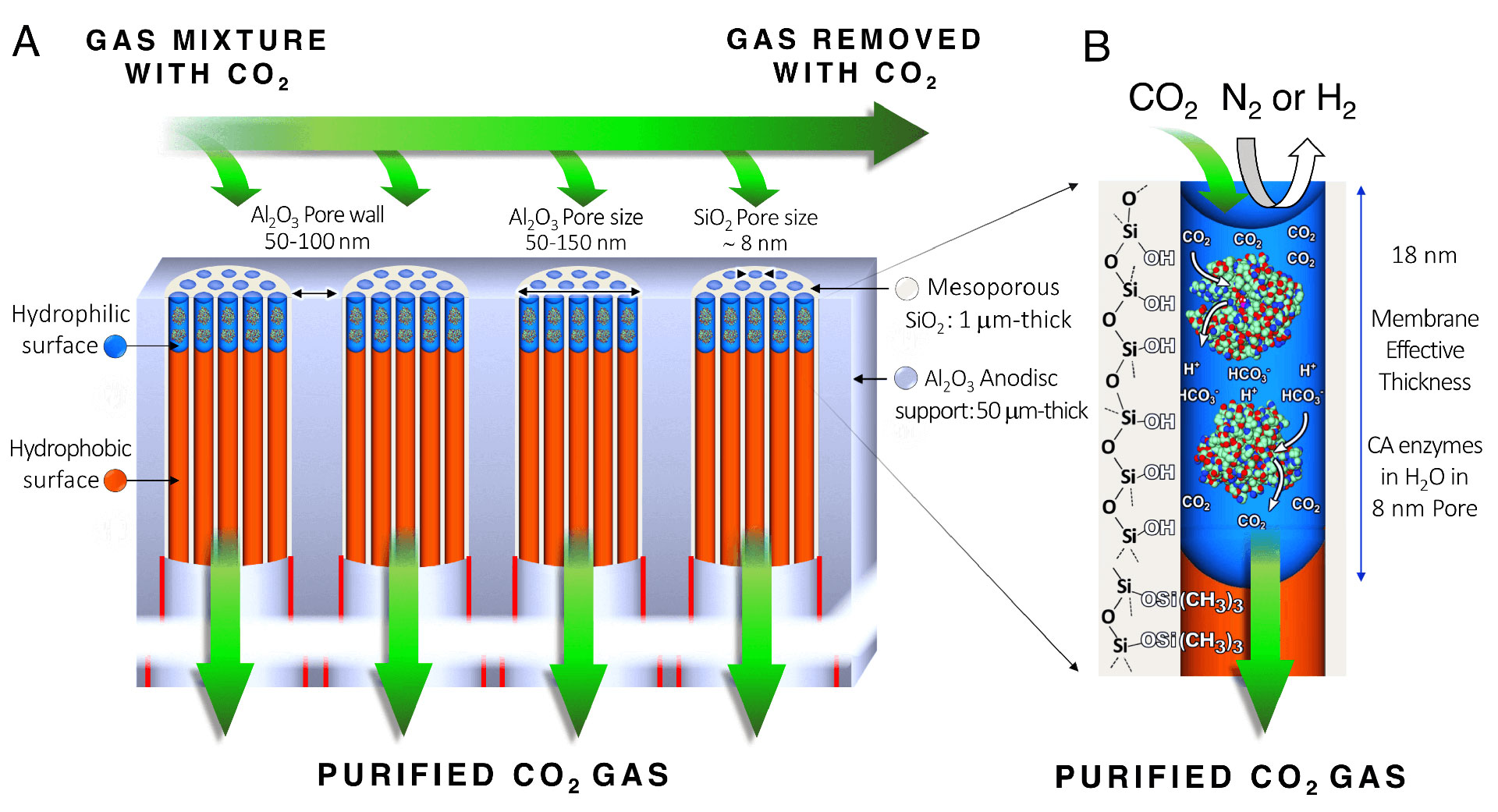
Biologically Inspired Membrane Purges Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences
Global Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Of Eight Different Download Scientific Diagram

Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization

Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Again Break Records c News

Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Livestock Poultry Livestock And Poultry Environmental Learning Community

Grain How Much Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Agriculture
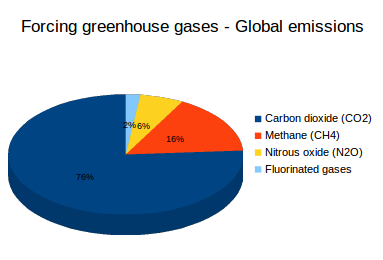
What Are Greenhouse Gases What S Your Impact

Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change
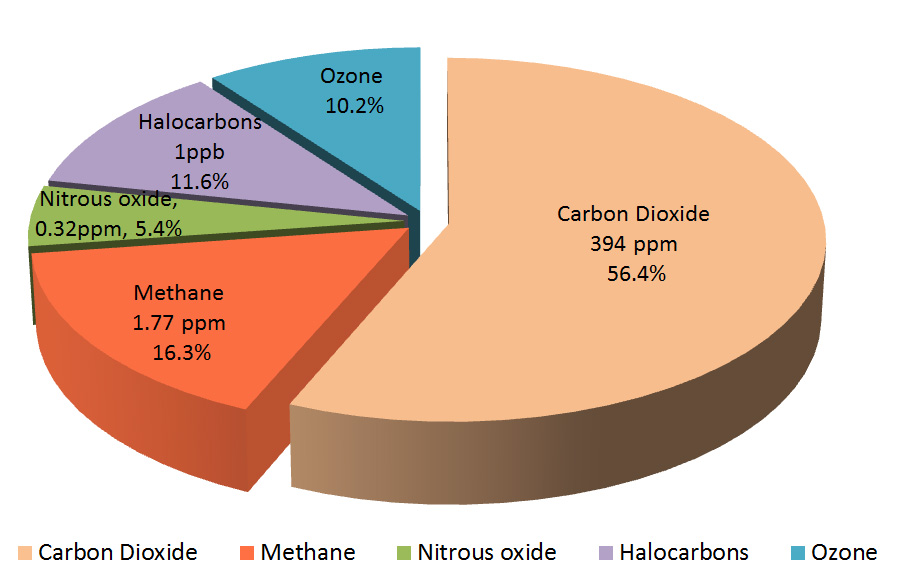
Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia

4 Ways To Cut Plastic S Growing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Insideclimate News

Q Tbn 3aand9gcthbmmuj2soduwj5i Zilr8kasetrna4smc5q Usqp Cau

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
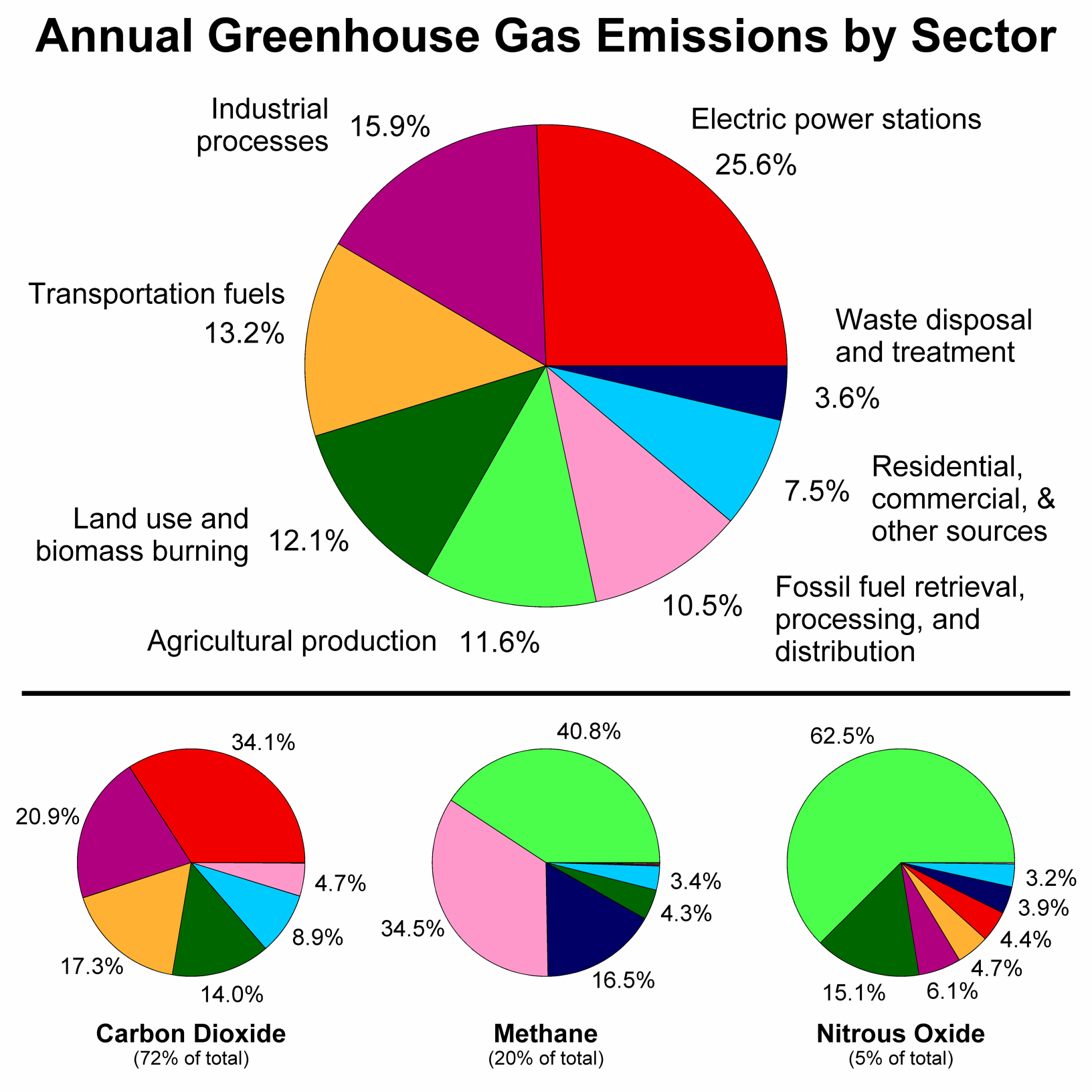
File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons

The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids

Windsor S Greenhouse Gas Emissions

The Principal Greenhouse Gases And Their Sources Neef

Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
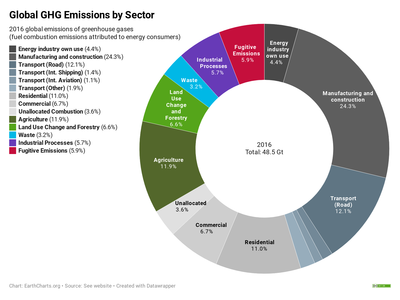
Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
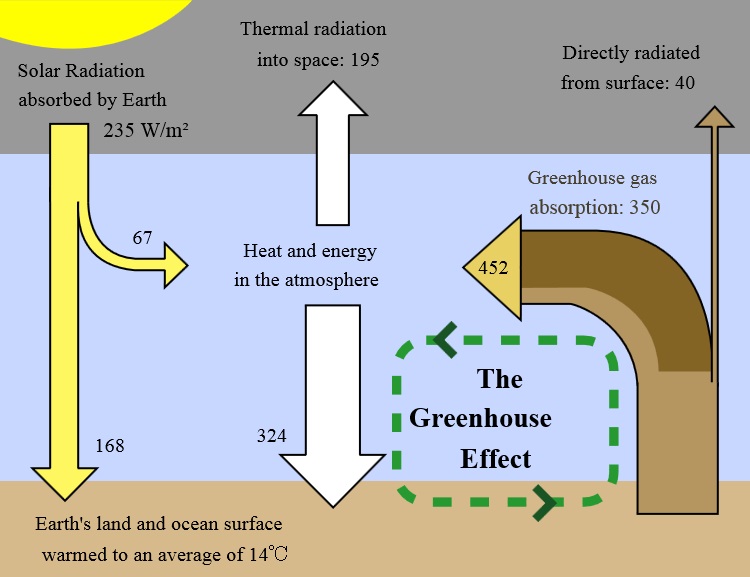
Anti Greenhouse Gasses Terraforming Wiki Fandom
Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
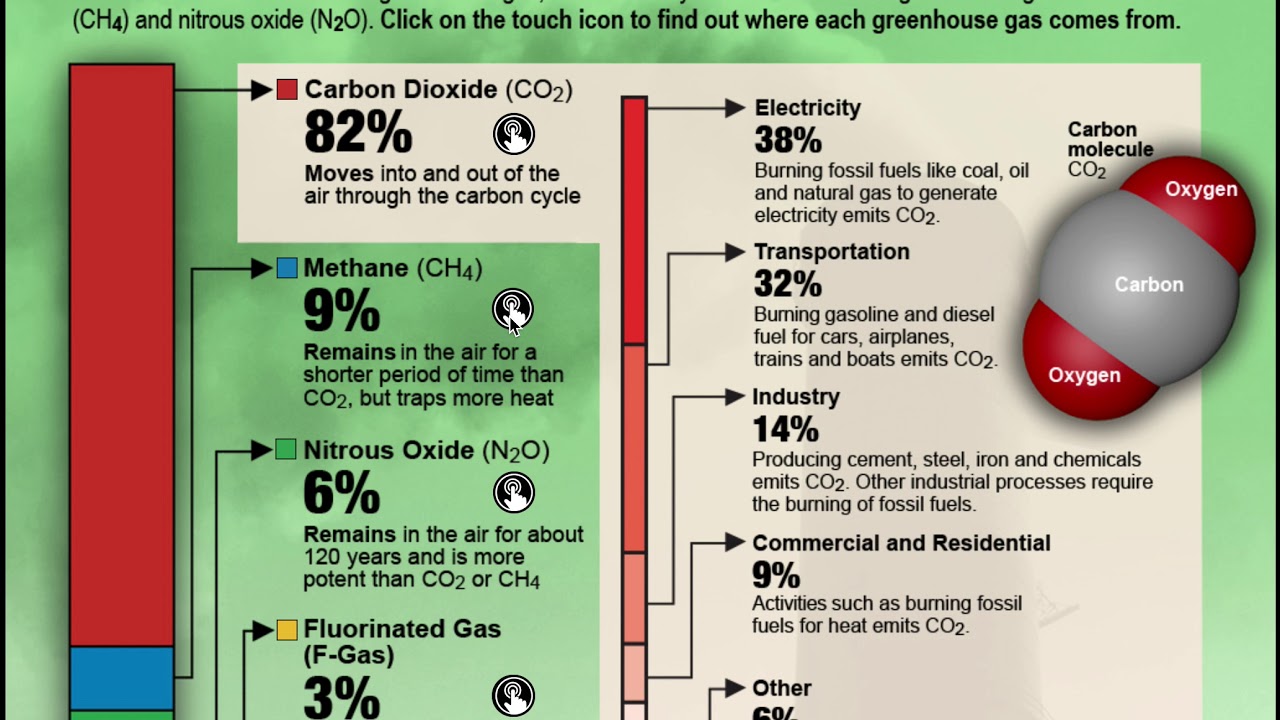
What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed
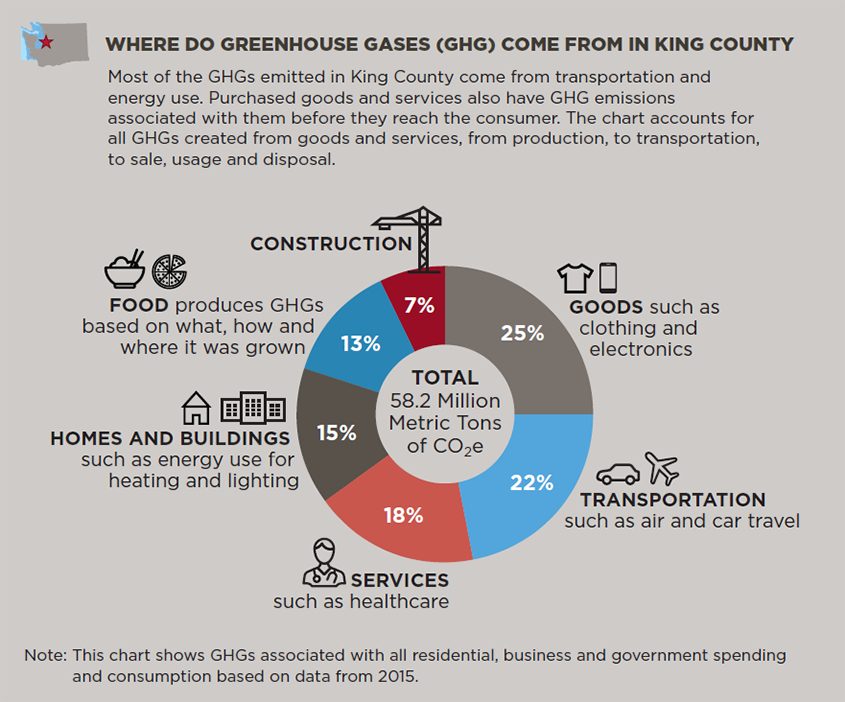
Greenhouse Gas Emissions In King County King County

Nahb Residential Greenhouse Gas Emissions
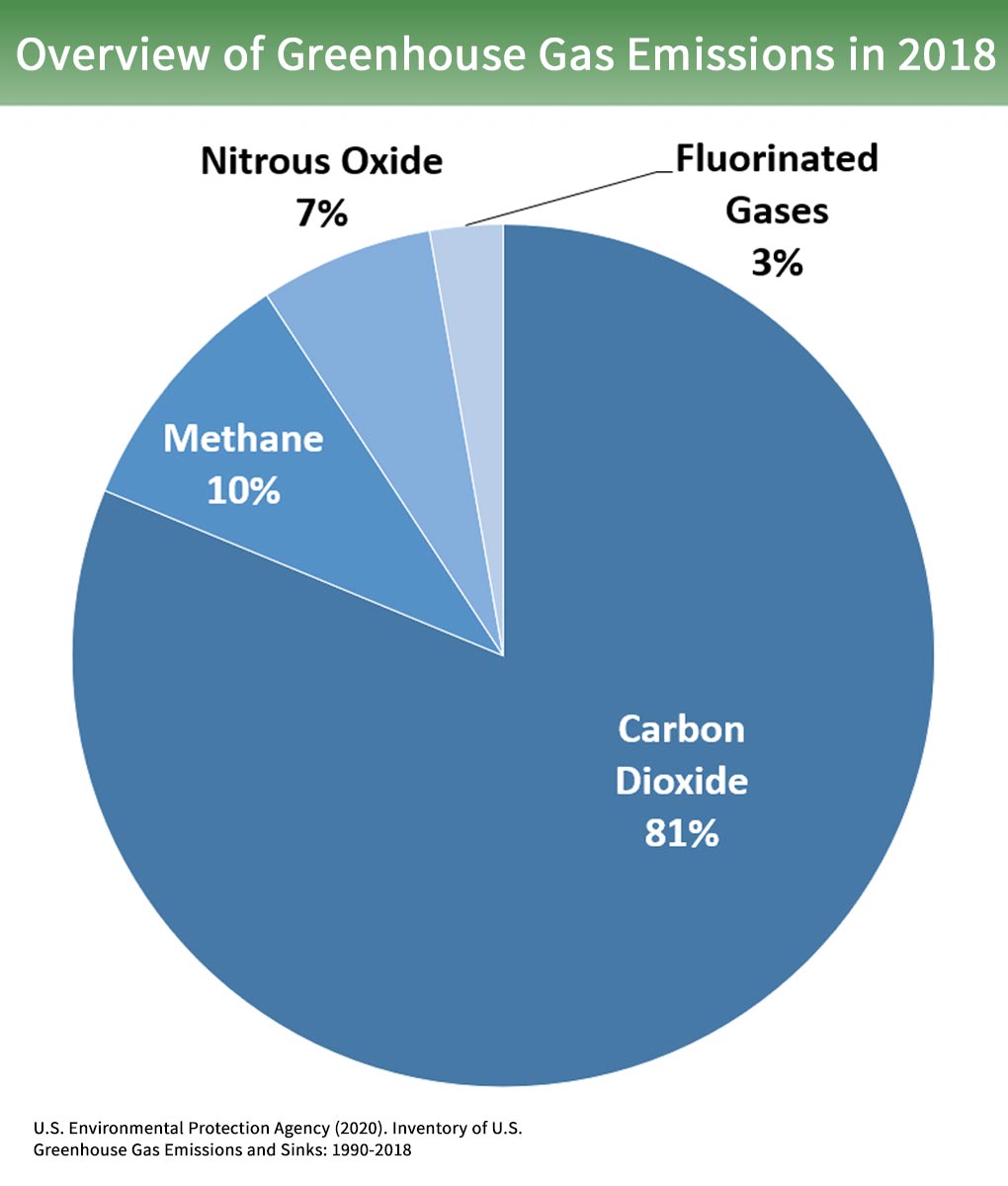
Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

The Unlikely Contributor To Minn S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Your Favorite Lake Mpr News

Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
Rescue Resource Efficient Pathways To Greenhouse Gas Neutrality Umweltbundesamt

Greenhouse Gases Bioninja

Banning The Super Greenhouse Gas Environment All Topics From Climate Change To Conservation Dw 17 10 16
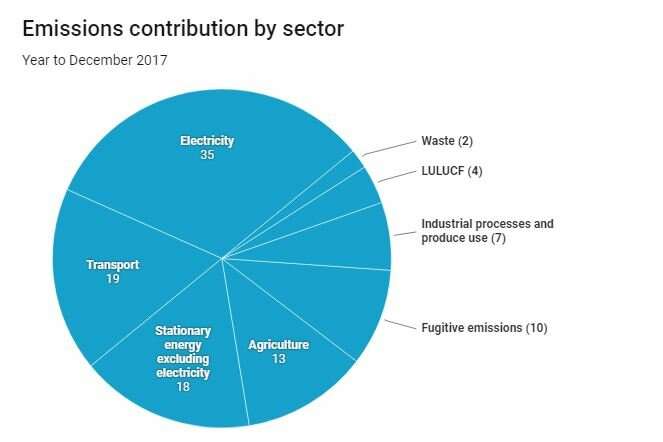
How To Neutralise Your Greenhouse Gas Footprint

Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate

The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia
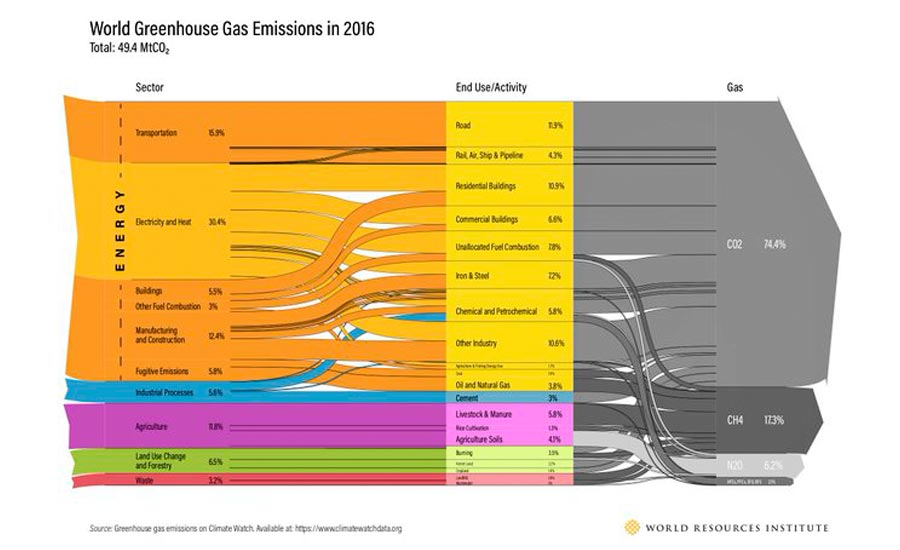
Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Data Is Interactive 02 07 Engineering News Record

Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From University Of California

Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Us Epa

Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
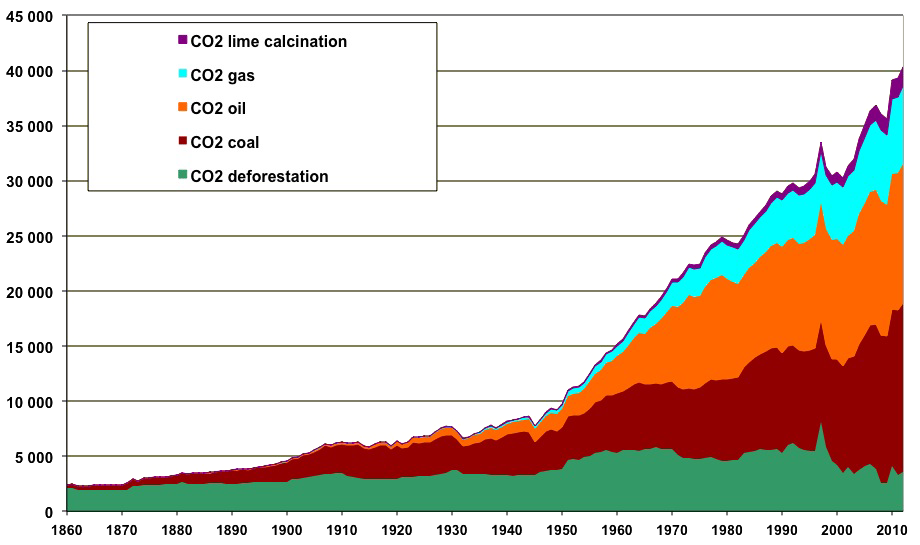
How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici

New Hampshire Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Climate Change Program Nh Department Of Environmental Services

Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate

Global Warming Impact On Greenhouse Gases Ag Decision Maker
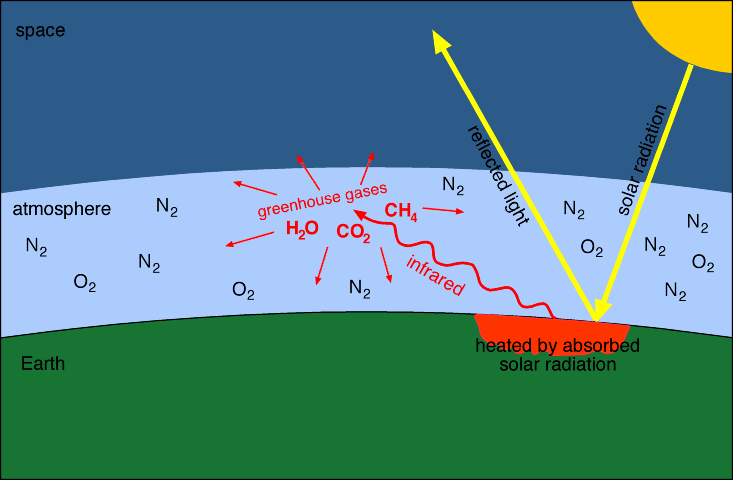
The Greenhouse Effect

Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute
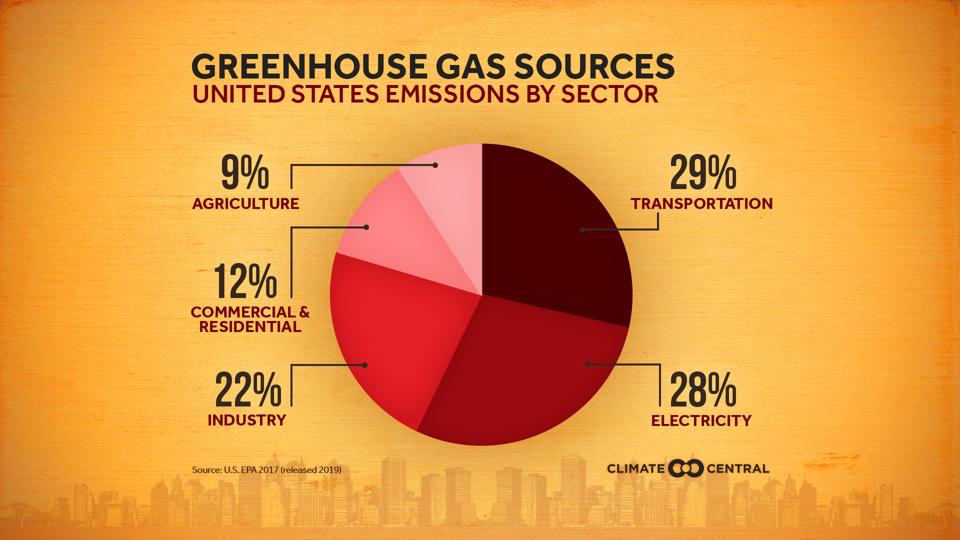
The Current Global Warming Trend Is Directly Related To Human Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases
1

Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know

Greenhouse Gas Emissions Sources Effects Conserve Energy Future

What Are Greenhouse Gases Main Sources And Climate Impact
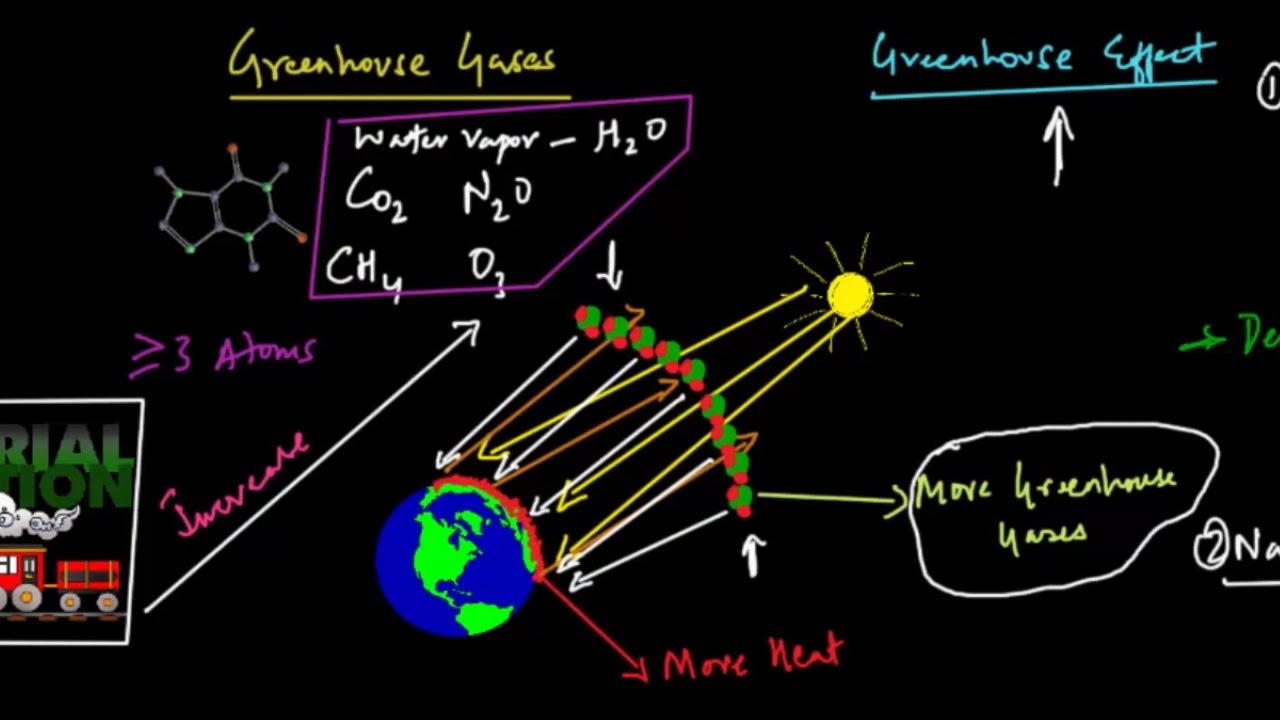
Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube

Greenhouse Gas Sources In The U S Wxshift

Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central

The Greenhouse Gases Airclim

Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases

Greenhouse Gases 101 Ben Jerry S

5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica

Procurement Organizations Have The Power To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions

Air Pollution Greenhouse Gases Britannica



