Moonmilk Cave Formation

Flowstone And Moonmilk Dales Rocks

Flowstone And Moonmilk Dales Rocks
Small Things Considered A Fascination With Caves
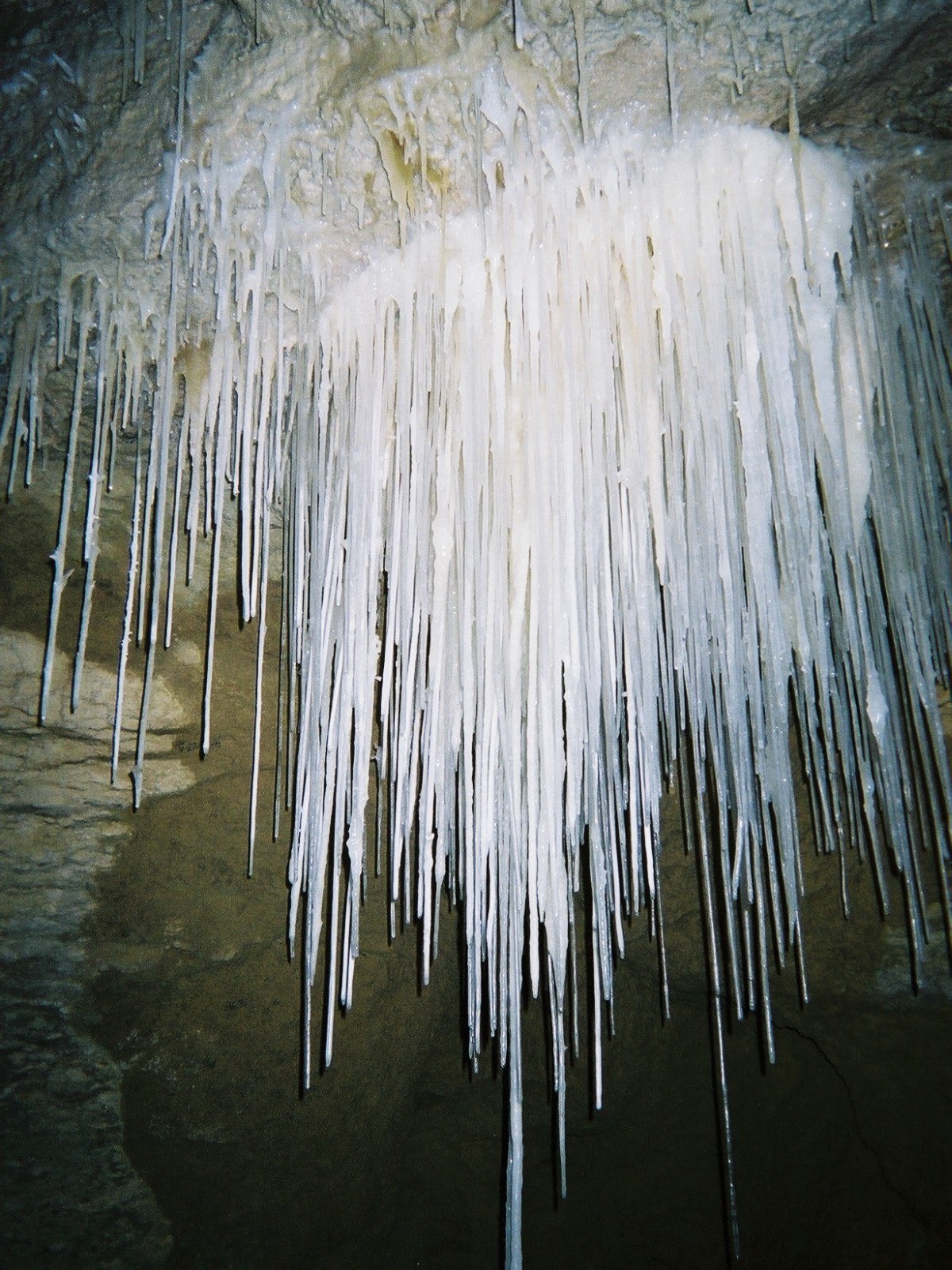

Soda Straw Wikipedia
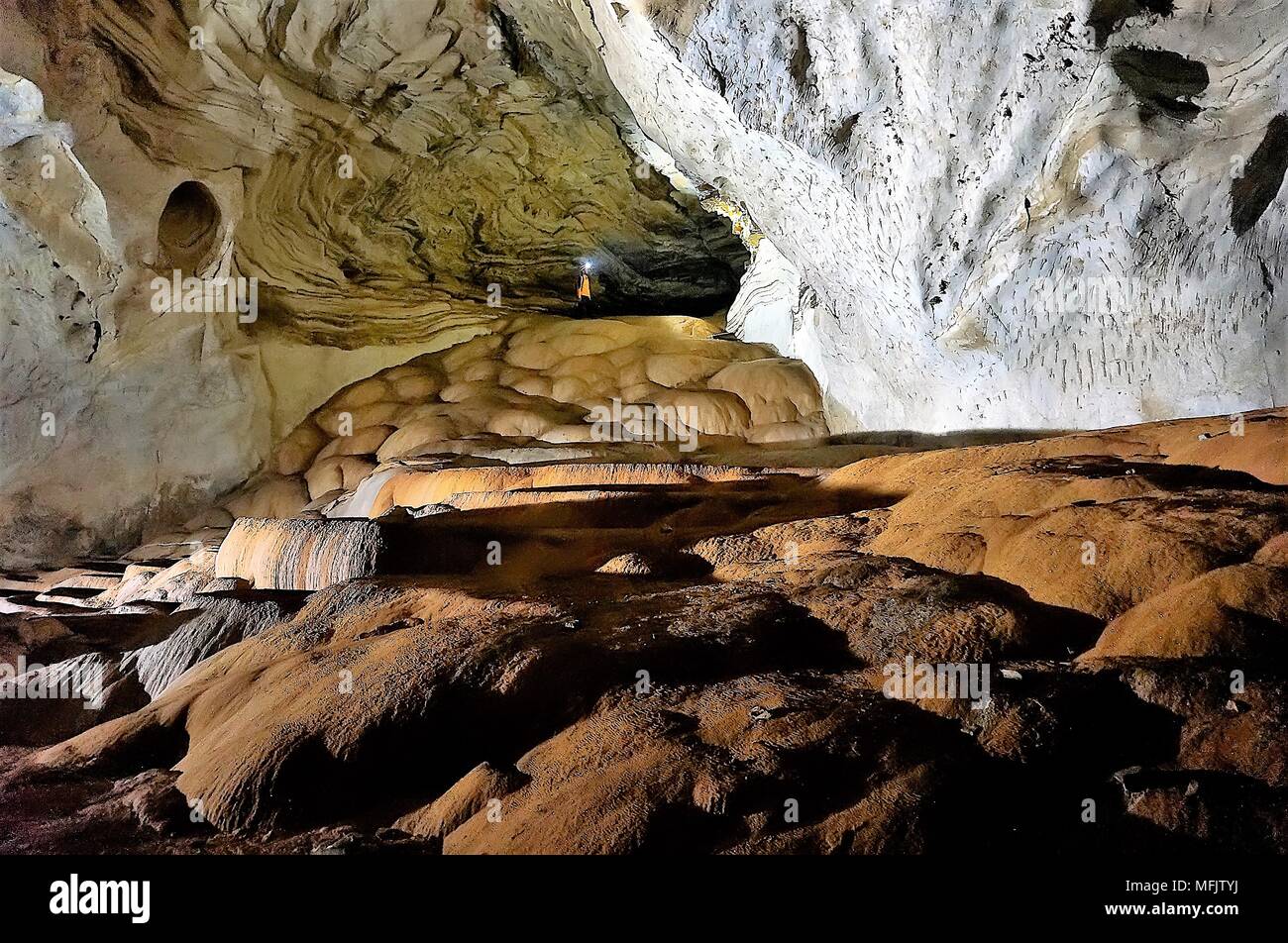

Moonmilk High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Flowstone Wikipedia
Their presence in the cave environment and also moonmilk was mentioned by Mulec et al.( 02).

Moonmilk cave formation. Moonmilk ostensibly created from Macromonas bipunctata in the cave Bergmilchkammer. Moonmilk, a bacteria-instigated precipitate of calcium carbonate, is one of the cave’s remarkable features. Rimstone A calcite deposit around the edge of a pool of water.
The limestone in the water is deposited on the hard surfaces, which are the rims of the fissure. Calcite moonmilk, which is a cave deposit formed of calcite crystals and water, is found in many caves in the Italian Alps. Calcite moonmilk, which is a cave deposit formed of calcite crystals and mater, is found in many caves in the Italian Alps.
Moonmilk is a very common cave deposit that probably precipitates from dripwater entering the cave, but forming very fine crytals rather than the larger ones typical of calcite deposits like flowstone. Their origin is not completely known but is likely related to moonmilk. Moonmilk is a karstic speleothem mainly composed of fine calcium carbonate crystals (CaCO 3) with different textures ranging from pasty to hard, in which the contribution of biotic rock-building processes is presumed to involve indigenous microorganisms.
When wet, moonmilk is pasty like cream cheese and has a high plasticity. Bacteria are able to induce carbonate precipitation although the participation of microbial or chemical processes in speleothem formation remains a matter of debate. These hydremagnesite bubbles are another unexplained feature of Jewel Cave.
Many kinds of moonmilk can be connected with the work of microorganisms, mostly. Bacon draperies, shaped and striped like their edible counterparts and " bird's nest " needle. These modern and ancient deposits are formed of fiber calcite crystals,.
‘Moonmilk’, often seen decorating the ceilings of Yorkshire caves, is, by contrast, a soft, creamy-white substance. Few caves in the National Park System offer a more stunning array of geological formations than Oregon Caves.Known as the "marble halls of Oregon," the rare marble cave was proclaimed a national monument in 1909.All six of the world's major rock types are found in the cave, along with a crystalline substance called "moonmilk.". The microbial diversity of karstic caves has been studied to understand the impacts of microbes on cave formation and to determine how this knowledge can be used for cave conservation 15–21.
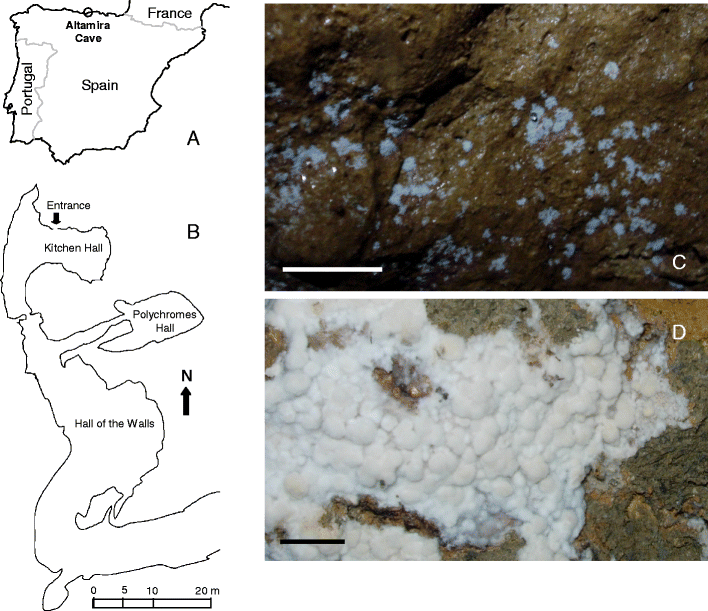
Role in moonmilk formation. 1 1 The role of microorganisms in the formation of calcitic moonmilk deposits and 2 speleothems in Altamira Cave 3 4 S. Cave balloons probably occur when solutions under pressure seap into a cave through cracks or out of porous walls of limestone.
"cave deposit"), commonly known as cave formations, are secondary mineral deposits formed in a cave.Speleothems typically form in limestone or dolomite solutional caves.The term "speleothem," as first introduced by Moore (1952), is derived from the Greek words spēlaion "cave" + théma "deposit". These results suggest that microbes may have important functional roles in subterranean environments. The total cavern size is 2.4 miles long, but the explored.
The Baeg-nyong cave is a natural limestone cave, which has long horizontal passages from the east to the west, including one main passage and three branches. Browse Expedia's selection of 3 hotels and places to stay closest to Moonmilk Cave. When cut in section, concentric growth rings can be seen.
At 21.16 feet, this thin, hollow stalactite beats the previous record of .47 feet, which was earned in an Australian cave. In this study, the origin of carbonate depositions such as moonmilk, an unconsolidated microcrystalline formation with high water content, and the consolidation of carbonate precipitates into hard speleothems were analyzed. It is possible that moonmilk is formed by water that dissolves and softens the karst of caves consisting of carbonates, and carries dissolved nutrients that can be used by microbes, such as Actinomycetes.
Rare and fragile type of cave formation, cave balloons are a small, gas-filled pouch made of hydromagnesite. Cave moonmilk deposits host an abundant and diverse actinobacterial population that has a great potential for producing novel natural bioactive compounds. Regarding microscopic fungi, no relation between the substrate (moonmilk) and a particular group of fungal species was proved.
Microbes in Cave Formations;. While there is controversy surrounding the processes that govern the formation of moonmilk, this biokarst is thought to be the result of physiochemi ‐. It is a precipitate from limestone comprising aggregates of fine crystals of varying composition usually made of carbonates such as calcite, aragonite, hydromagnesite, and/or monohydrocalcite.
In the bottom of a sinkhole they found a narrow crack leading into the hillside. Moonmilk.” Today, moonmilk still exists in caves all over the world, with the largest formations found in Arizona;. In November 1974 two young cavers, Gary Tenen and Randy Tufts, were exploring the limestone hills at the base of the Whetstone Mountains.
A series of four articles explaining the role of microorganisms in for Descent Magazine, the world's most popular magazine for people interested in caves and caving. The presence of microorganisms in moonmilk formations has been observed in caves around the world, from the tropics to high latitudes. A limestone cave contains various types of speleothems, such as soda straw, stalactite, stalagmite, and moonmilk, all of which are mainly composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO 3 ).
Moonmilk forms crusts on walls and floors, sometimes stalactites and stalagmites. Consistency of cream cheese when wet, delicate and powdery when dry. Kartchner Caverns med by water flowing over a bump on the wall, then dripping to create this beautiful formation.
The Long Churn Caves:. Phreatic zone The region, below the water table, in which rock is saturated with water. Cave bacteria could help develop future antibiotics.
A rare type of cave formation, balloons are a small, gas-filled pouch usually made of hydromagnesite. Moonmilk A rare form of hydromagnesite or calcium carbonate which is semisolid. Besides, the existence of complex microbial communities thriving in cave environments has been highlighted 2.
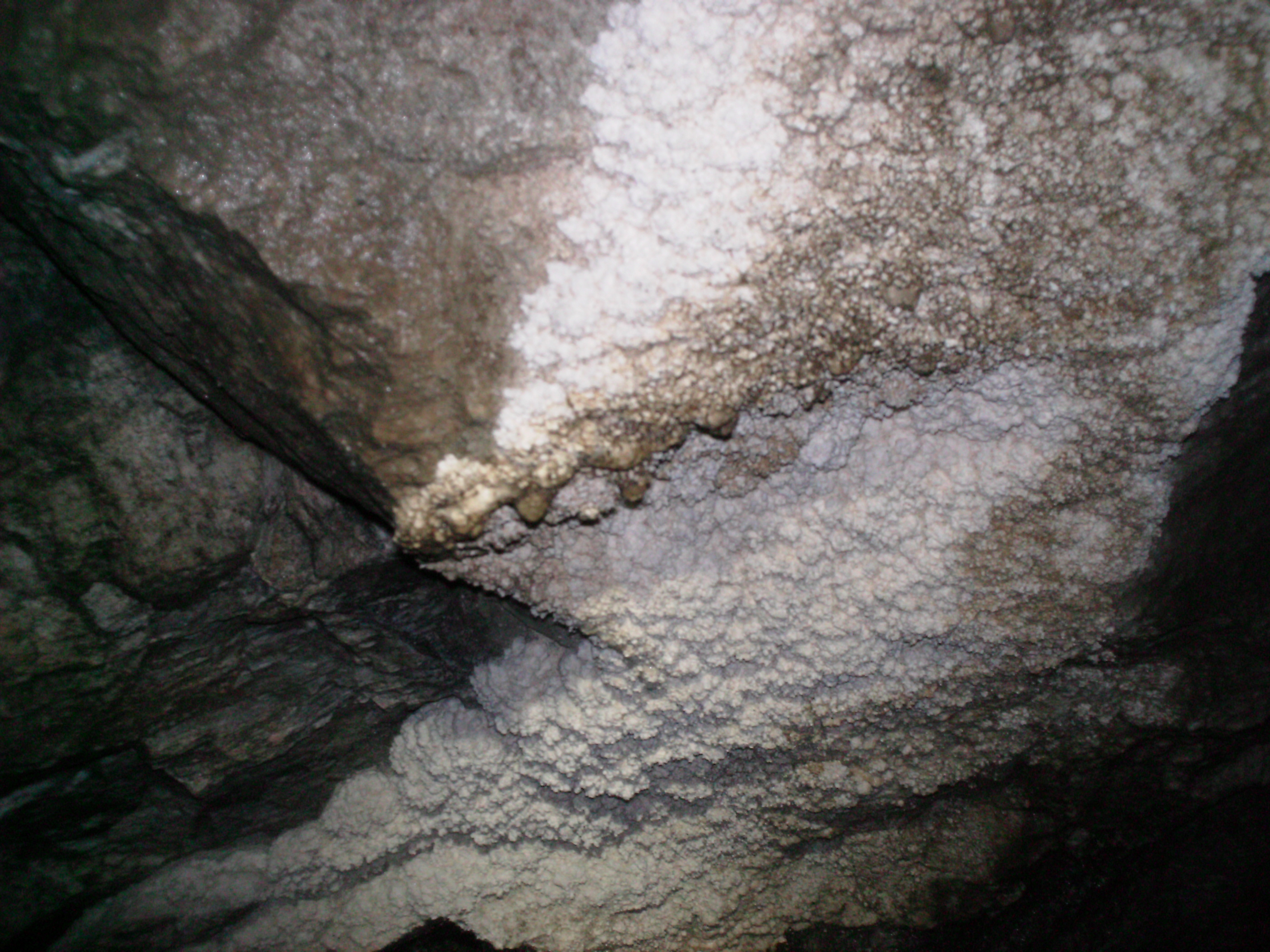
Moonmilk (sometimes called mondmilch, also known as montmilch or as cave milk) is a white, creamy substance found inside limestone, dolomite, and possibly other types of caves. Moonmilk is made of very fine, white crystals, usually carbonites such as calcite or hydromagnesite. Moonmilk, which is often seen coating walls in temperate caves, is a porous secondary calcite deposit composed of an aggregate of microcrystalline calcite and water.
Perhaps unique to Jewel Cave is a form of it which resembles a silvery bubblegum. In the present review, we provide a summary of geomicrobiological work done so far in some Indian caves. Therefore, studying microbial communities in different states of moonmilk can provide information on the microorganisms involved in moonmilk formation.
Various compositions have been reported including common cave minerals such as calcite, aragonite and. Moonmilk is a type of cave forma‐ tion with a soft cottage cheese texture and appearance. Moonmilk was originally explained as created by " moon rays".
Often resembling marine coral. Moonmilk is currently defined as a microcrystalline aggregate cave deposit with variable mineralogy, a high water content, a high porosity, and distinguishable macro- and micro-texture (Hill & Forti, 1997). Moonmilk is a magnesium carbonate compound, not uncommon in caves.
Find cheap deals and discount rates among them that best fit your budget. It has been found that microbes participate in formation of the white and soft secondary calcite (calcium carbonate) deposits that can coat the walls, floors, and ceilings of caves. Some studies suggested fungi as the major participants in the process 7, although more recent investigations proposed bacteria as the major inducers of carbonate deposition forming moonmilk in caves 2, 9.
The biochemical activity of both microbial members might be inconsiderable in the formation of moonmilk. Moonmilk, a living mineral formation, covers a wall in Windgate Cave on Prince of Wales Island, Alaska. This study, based on moonmilk deposits found in Caverne de l'Ours, Ottawa Valley region, proposes a model for its formation based on the calcite and water isotope chemistry and.
Maciejewska and coauthors (15) reported the isolation of the strain Streptomyces lunaelactis sp. These modern and ancient deposits are formed of fiber calcite. Gonzalez2* 6 7 1 Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales, MNCN-CSIC, Jose Gutierrez Abascal 2, 8 Madrid , Spain 9 2 Instituto de Recursos Naturales y Agrobiología.
Carbon dioxide is released into the cave air, then the water starts to vaporize slowly. As can be seen in the photo below, moonmilk may take on shapes somewhat like those of flowstone. About 95% of moonmilk deposits are carbonatic and its most common type is calcite moonmilk.
Microbe-mineral interactions in caves can lead to secondary mineral formations such as speleothems, moonmilk etc. Many studies have demonstrated the role of microbial and physicochemical activities in the formation of CaCO 3 ( Anbu et al., 16 ). However, the true nature of its creation and why it never solidifies remains a scientific mystery.
The definition of "speleothem," in. It's simple to book your hotel with Expedia. A general necessity of the formation of Shields is an extremely slow but almost constant flow of water.
Save on popular hotels near Moonmilk Cave, Mulu:. Ingleborough’s caves and potholes;. It's also the nursery roost for female cave myotis bats from mid-April through mid-October, during which time this lower cave is closed.
It is formed by the deposition of calcite and other minerals from the dripping water, but unlike the crystals of sinter, those crystals are loosely connected rods of 1 x 8 micrometers. Popcorn Nodules of mineral deposits formed in such a way as to resemble popcorn. Calcite moonmilk, which is a cave deposit formed of calcite crystals and water, is found in many caves in the Italian Alps.
The Big Room presents the largest formation of brushite moonmilk and the first reported occurrence of " turnip " shields. Calcifying bacteria on moonmilk speleothem formation in the Grotta Nera are reported for the first time. The Majella Massif hosts a complex karst system of several caves;.
The accessible Grotta Nera is the most interesting one. From moonmilk speleothem collected in the. In caves, microbially induced mineralization is documented in the formation of carbonates, moonmilk, silicates, clays, iron and manganese oxides, sulfur, and saltpeter at scales ranging from the microscopic to landscape biokarst.
Cave are extreme and specialised habitats for terrestrial life that sometime contain moonmilk, a microcrystalline cave speleothem with variable mineralogy, a high water content, a high porosity, and distinguishable macro- and micro-textures. We frequently observed "moonmilk" around roots where they emerged from the bedrock. These modern and ancient deposits are formed of fiber calcite crystals, 50-500 nm wide and 1 to > 10 µm long, and polycrystalline chains that have few crystal defects.
Cave temperature is only slightly cooler in winter than in summer, but in contrast to above-ground winter conditions, a winter visitor finds the cave relatively warm. Their origin is not completely known, but is likely related to moonmilk, a material of high plasticity.Balloons probably occur when solutions under pressure seep into a cave through cracks or out of porous walls of limestone. Speleothems (/ ˈ s p iː l iː ə θ ɛ m /;.
Reactions to acid eating rock away, heat melts rock. In our previous attempt to isolate culturable moonmilk-dwelling Actinobacteria, only Streptomyces species were recovered, whereas a metagenetic study of the same deposits revealed a complex actinobacterial community including 46. Formation of caves is called.
Active cave, dead cave, dormant cave, fault cave, fissure cave, glacial cave, grot-hole, ice cave, lava cave, limestone cave and live cave. Big Room cave tours are closed during the summer for several months (April 15 to October 15) each year because it is a nursery roost for cave bats, however the Throne Room tours remain open year-round. Legend says that the Native American.
The Big Room contains the world's most extensive formation of brushite moonmilk. An appointment with Doctor Bannister;. This type of speleothem has branching stems and nodular tips;.
But the theory of it being produced by the rays of the moon has lost some of its popularity. Moonmilk is a consistency of what. Because Cave Popcorn is one of the few cave formations that can form both in the open air and under water, the current scientific theory is that the calcite-laden water is forced out of the walls from internal pressure.
What does physical erosion mean. Moonmilk is a karstic speleothem mainly composed of fine calcium carbonate crystals (CaCO3) with different textures ranging from pasty to hard, in which the contribution of biotic rock-building processes is presumed to involve indigenous microorganisms. Because the slightest touch will harm the delicate formations, especially Moonmilk.
The results revealed considerable bacterial and fungal diversity associated with moonmilk in a karstic cave system, suggesting that the microbial community implicated in moonmilk formation may be more diverse than previously thought. What can support the life of microorganisms. The Potential of Cave Microbes.

Nakimu Caves Columbia Mountains Institute Of Applied Ecology
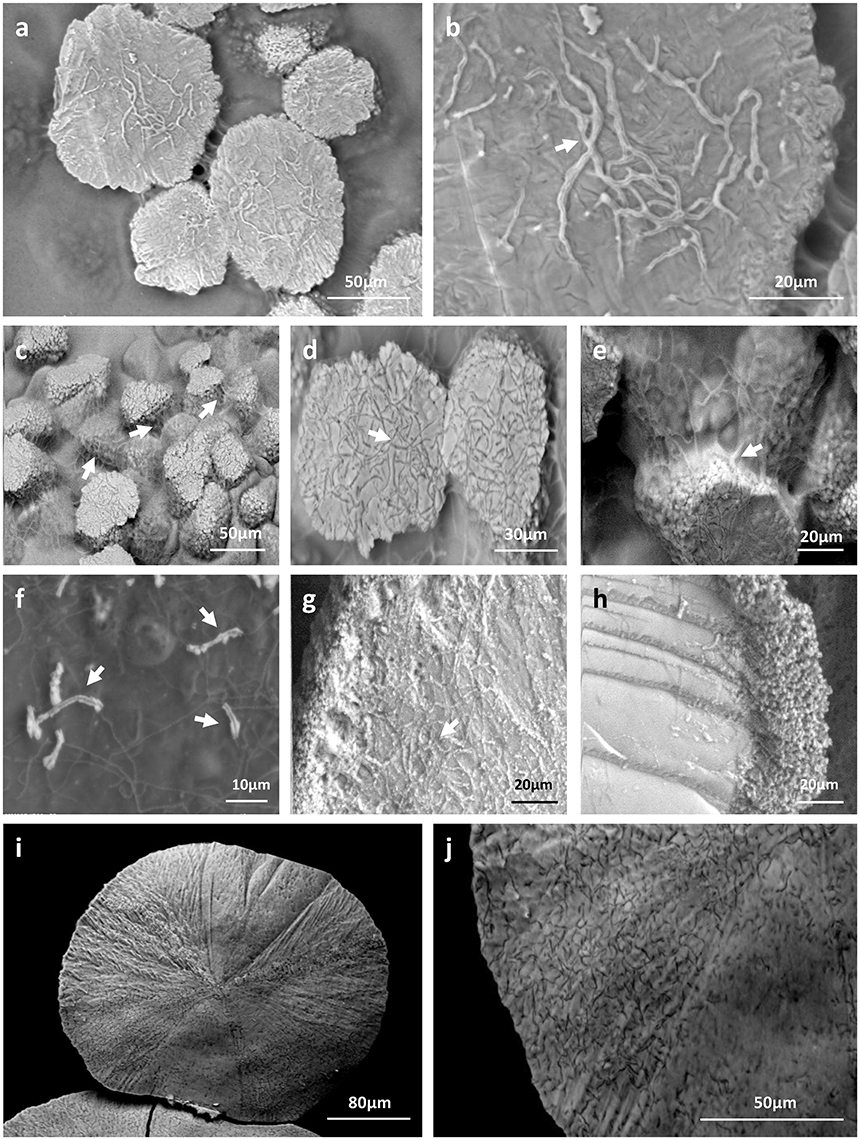
Frontiers Assessment Of The Potential Role Of Streptomyces In Cave Moonmilk Formation Microbiology
Pdfs Semanticscholar Org A368 C2cec57f7dc93aba6f3caf695e0eb6d42ad6 Pdf

Pdf Calcite Moonmilk Crystal Morphology And Environment Of Formation In Caves In The Italian Alps

Field Photographs Of The Speleothems At The Ecce Homo Hill S Cave A Download Scientific Diagram
Hillock The Cave With The Largest Stalactite In Europe Senderismoeuropa Com
Scholarcommons Usf Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 2175 Context Ijs

Moonmilk Mcginley Ryan Amazon Com Books

Cave Wikipedia

Snow Cave Zgornja Savinjska Dolina
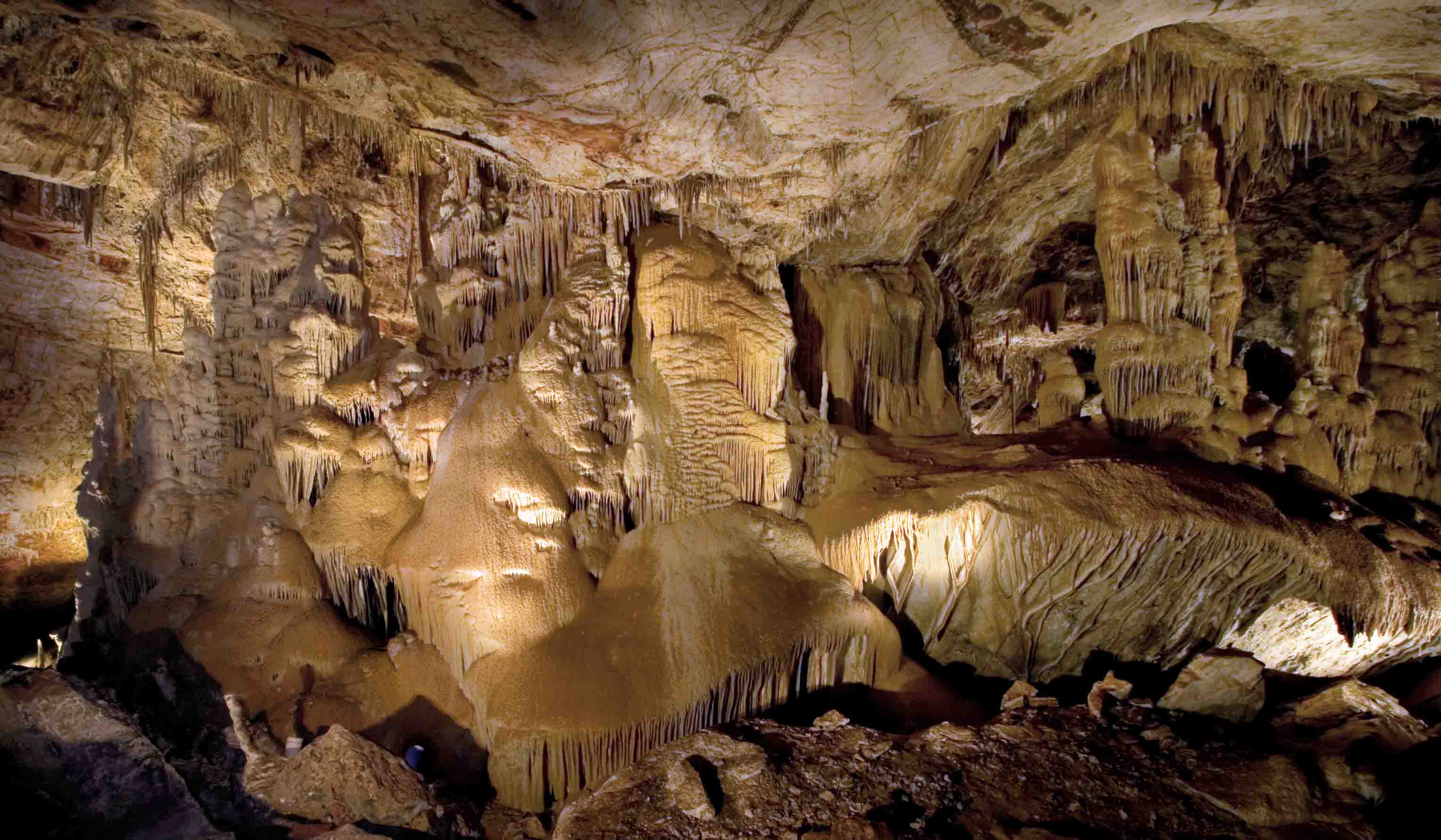

Kartchner Caverns State Park Wikipedia

Caverns Of Sonora Moon Milk Falls Located 8 Miles 13 Km Flickr
Caves Org Pub Journal Pdf V76 Cave 76 02 Pdf

Cave Information Kartchner Caverns State Park

Moonmilk Wikipedia

Pdf Allophane Moonmilk From A Granite Gneiss Cave In Norway A Biogenic Intermediate In Deep Weathering Stein Erik Lauritzen Academia Edu

The Virtual Cave Moonmilk

The Park Is One Gigantic Cave Filled With Palaeozoic Rock Formations Containing What Are Called Stala With Images Kartchner Caverns Traveling By Yourself Ranch Vacations

Nixlucke Teton Gravity Research

12 Moonmilk In Altamira Cave Spain Most Likely Of Biological Origin Download Scientific Diagram

Scientists Are Spelunking For Cave Gunk To Fight Superbugs Popular Science

Skiing The Planet August 18

Moonmilk Wikipedia

A Cave Entrance B Stalactites And Stalagmites In A Gallery C Cave Download Scientific Diagram

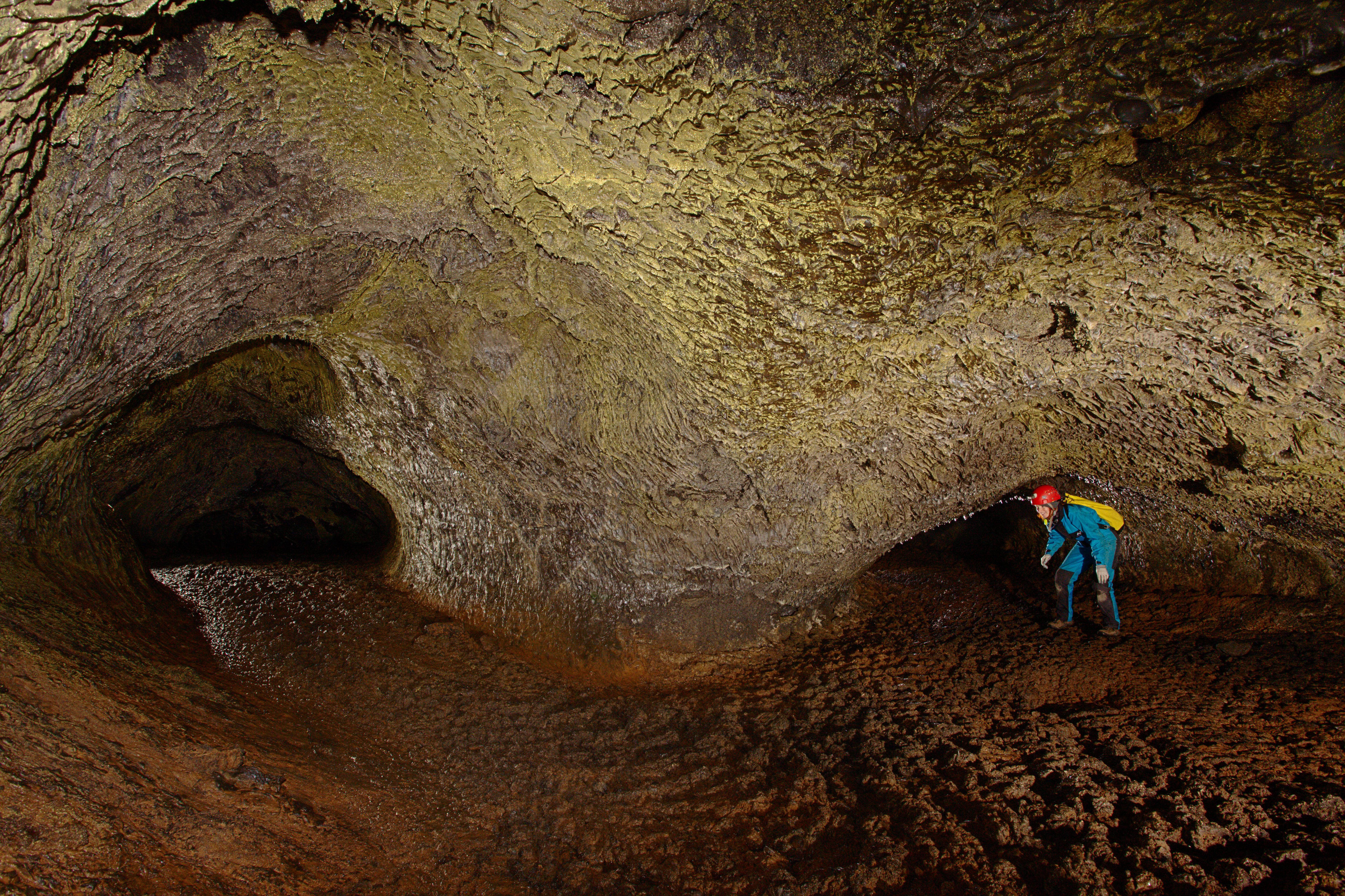
Moonmilk Cave Photo

The Only Moonmilk River In The World

Ryan Mcginley Moonmilk Love Art Art Culture Art
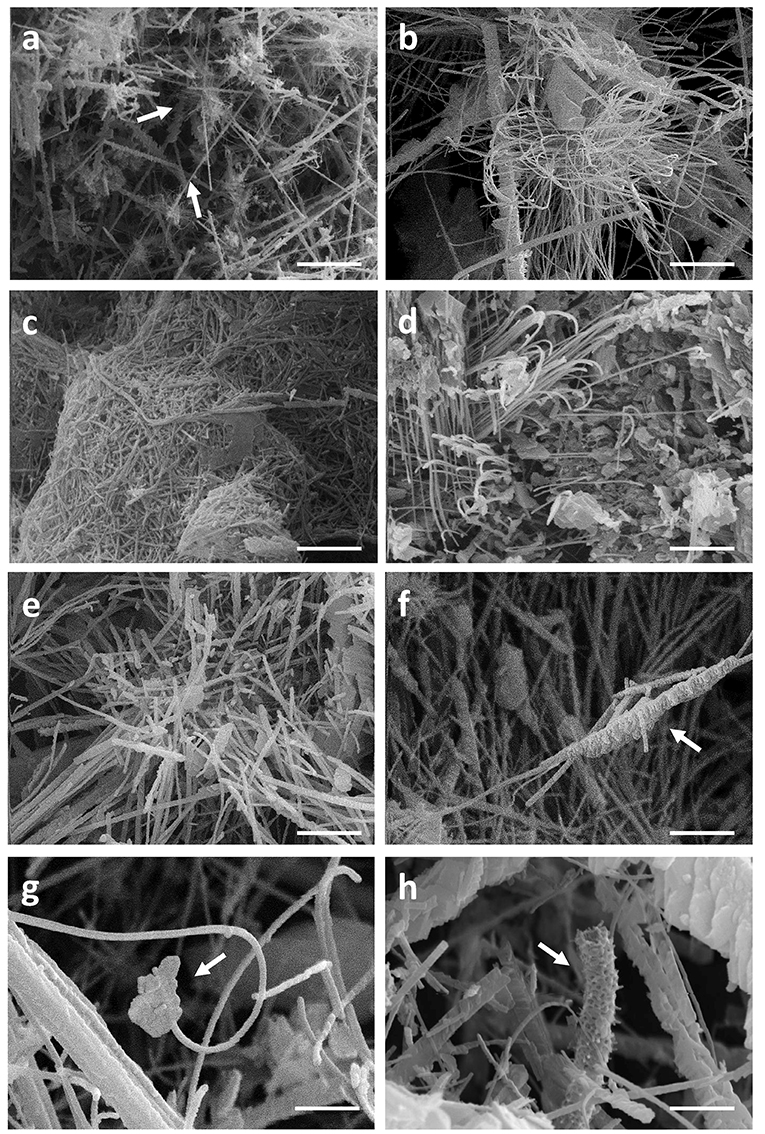
Frontiers Assessment Of The Potential Role Of Streptomyces In Cave Moonmilk Formation Microbiology

Flowstone And Moonmilk Dales Rocks
Small Things Considered A Fascination With Caves

Kartchner Caverns Microbial Observatory Research Background The University Of Arizona

Stora Skuggan Moonmilk Review

An Elusive State Of Being Moonmilk Revisited Dare

Figure 1 From Role Of The Microbial Community In Formation Of Speleothem Moonmilk In The Snezhnaya Carst Cave Abkhazia Semantic Scholar

Moonmilk The Mysterious Substance Lying In Caves Youtube

Crater Lake National Park Nature Notes 1995

Figure 2 From Archaeal Distribution In Moonmilk Deposits From Alpine Caves And Their Ecophysiological Potential Semantic Scholar

Cavern Wonders More Geology For Today Dr Tambra L Eifert
Caves Org Pub Journal Pdf V76 Cave 76 02 Pdf

Album Skunk Hollow Moon Milk

How Ryan Mcginley Creat His Moon Milk Project Photo Net Photography Forums

Active Moonmilk Moonmilk Is An Actinomyces Bacterial Growt Flickr

Moon Milk And Caramel Sherri Langford Swf Flickr
Small Things Considered A Fascination With Caves

Moonmilk High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Snow Cave Zgornja Savinjska Dolina
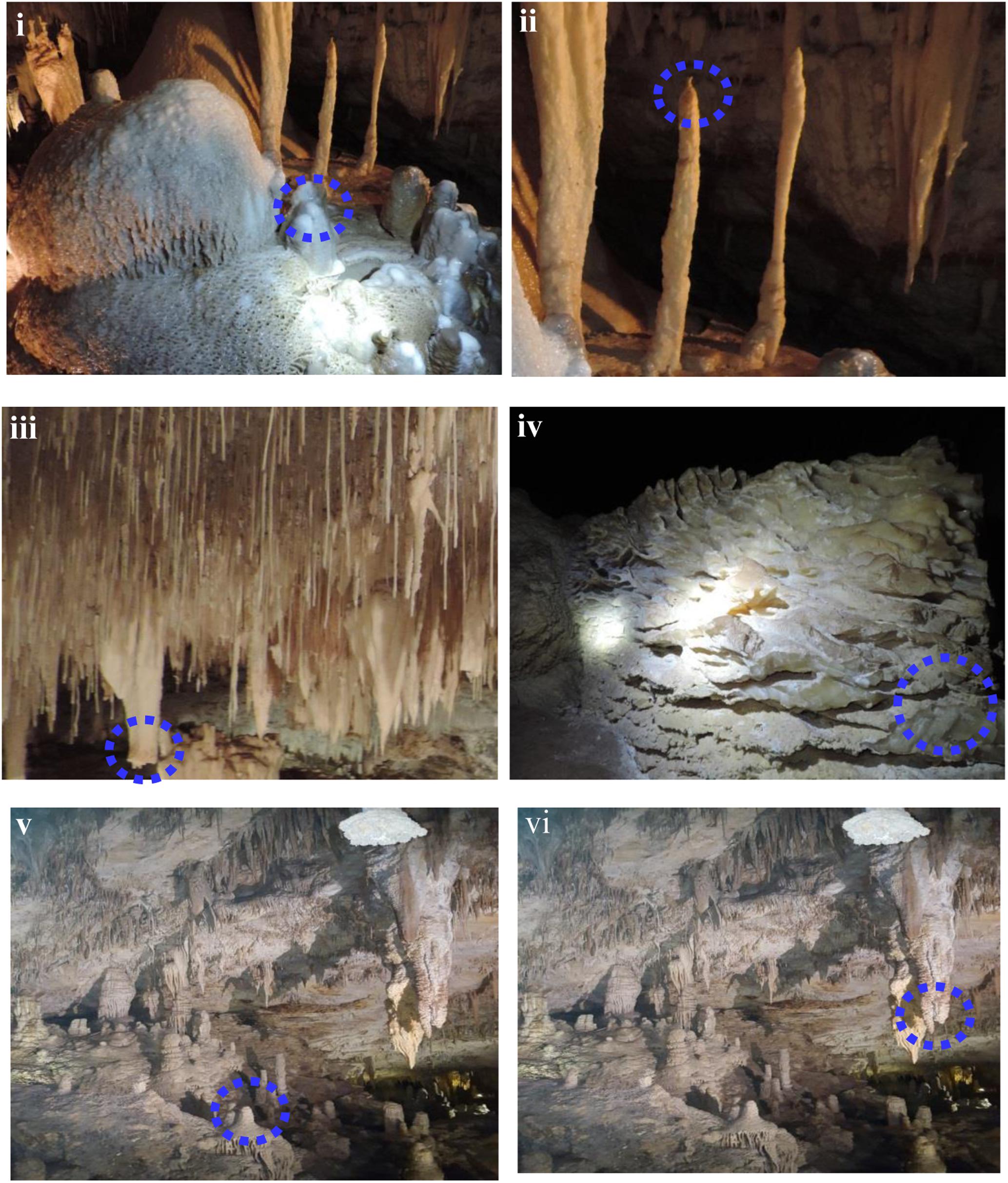
Frontiers Microbial Diversity And Mineralogical Mechanical Properties Of Calcitic Cave Speleothems In Natural And In Vitro Biomineralization Conditions Microbiology

Moonmilk In A Lava Cave 3 Lava Fine Art America Cave

Cave Minerals Analyzed In El Soplao Cave By Raman Spectroscopy A Download Scientific Diagram

Pdf The Role Of Microorganisms In The Formation Of Calcitic Moonmilk Deposits And Speleothems In Altamira Cave Semantic Scholar

Moonmilk Going Underground With Ryan Mcginley Art And Design The Guardian

Moonmilk Going Underground With Ryan Mcginley Art And Design The Guardian

Identifying Tree Roots In The Caves Of Quintana Roo Mexico As A Step Toward Ecological Insights And Improved Conservation Adams Plants People Planet Wiley Online Library

Cavern Wonders More Geology For Today Dr Tambra L Eifert

12 Moonmilk In Altamira Cave Spain Most Likely Of Biological Origin Download Scientific Diagram
Caves Org Pub Journal Pdf V76 Cave 76 02 Pdf

Page 2 Moonmilk High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

The Only Moonmilk River In The World
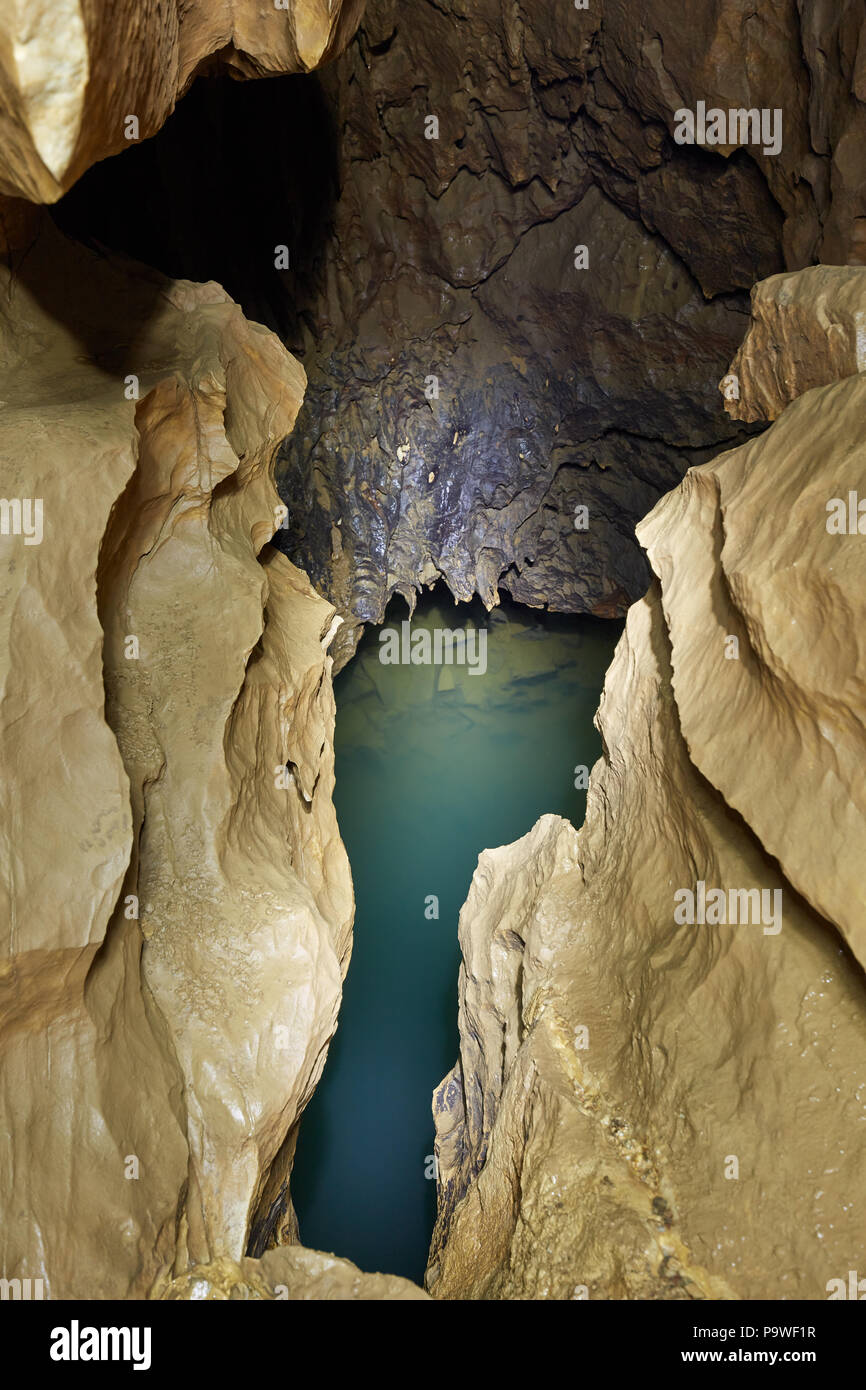

Page 2 Moonmilk High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Ryan Mcginley Morel

Speleothem Types Observed In The Perama Cave A Speleogens B Download Scientific Diagram

Figure 5 From Microbiological Activities In Moonmilk Monitored Using Isothermal Microcalorimetry Cave Of Vers Chez Le Brandt Neuchatel Switzerland Semantic Scholar

Speleothems Moonmilk

Moon Milk Cave Formation Youtube

Kartchner Caverns State Park
A Three Peaks Up And Under
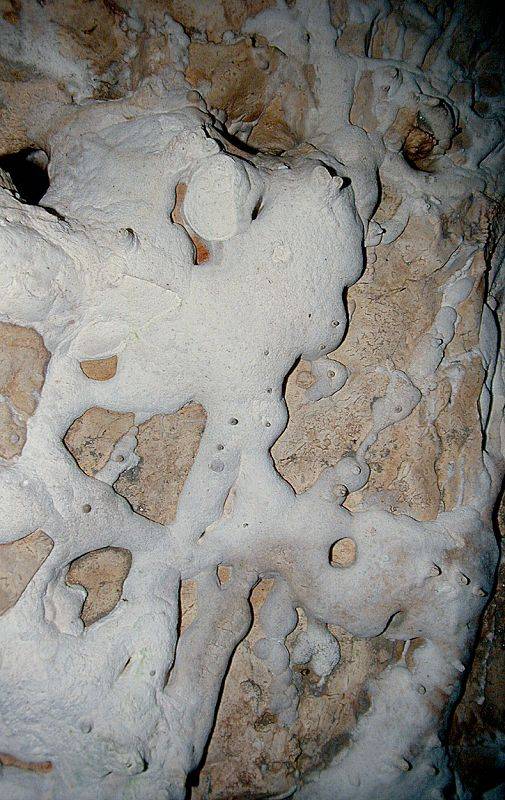

Speleothems Moonmilk
Caves Org Pub Journal Pdf V76 Cave 76 02 Pdf

Moonmilk Caves Gunung Mulu Mrthomson Flickr

The Role Of Microorganisms In The Formation Of Calcitic Moonmilk Deposits And Speleothems In Altamira Cave Sciencedirect

Cave Information Kartchner Caverns State Park

Flowstone And Moonmilk Dales Rocks

Moonmilk No Algar Da Figueira Macico Calcario Estremenho Youtube

Pdf Calcite Moonmilk Crystal Morphology And Environment Of Formation In Caves In The Italian Alps Andrea Borsato Academia Edu

Pdf Calcite Moonmilk Crystal Morphology And Environment Of Formation In Caves In The Italian Alps

Moonmilk In A Lava Cave 3 Photograph By Tonya Hance

A Moonmilk Columns And Stalactites In The Rear Part Of Nixofen The Download Scientific Diagram

Canmore Cave Tours Everyone Knows What A Stalactite And Stalagmite Are But Do You Know What Flowstone Moonmilk Or Coralloids Are Follow Us Down Into The Depths Of Rat S Nest

Have An Underground Adventure At Kartchner Caverns Experience Arizona

Moonmilk Cave Mulu Nationalpark Borneo Malaysia Flickr

096 Moonmilk Passage We Followed The Voices Deeper Into Th Flickr

Caverns Of Sonora Moon Milk Both Chocolate Vanilla Flickr
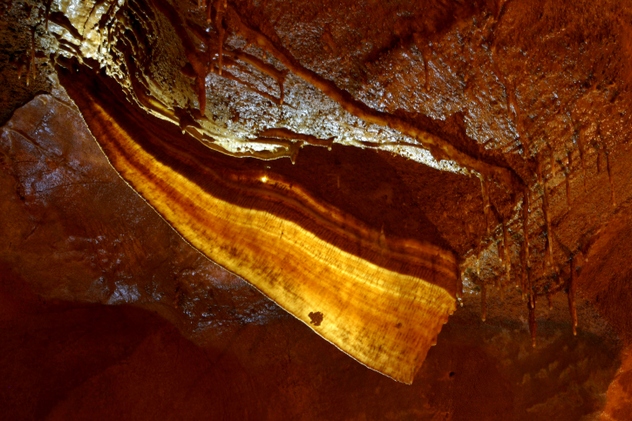

10 Astonishing Cave Formations Listverse
Page 2 Moonmilk High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy

Moonmilk Heart The White Is The Dried Remnants Of An Actin Flickr

Mulu National Park Borneo 06 Moon Milk Cave Because Of The White Fungus That Grows On Limestone Formations Photo
Moonmilk Deposits Originate From Specific Bacterial Communities In Altamira Cave Spain Springerlink
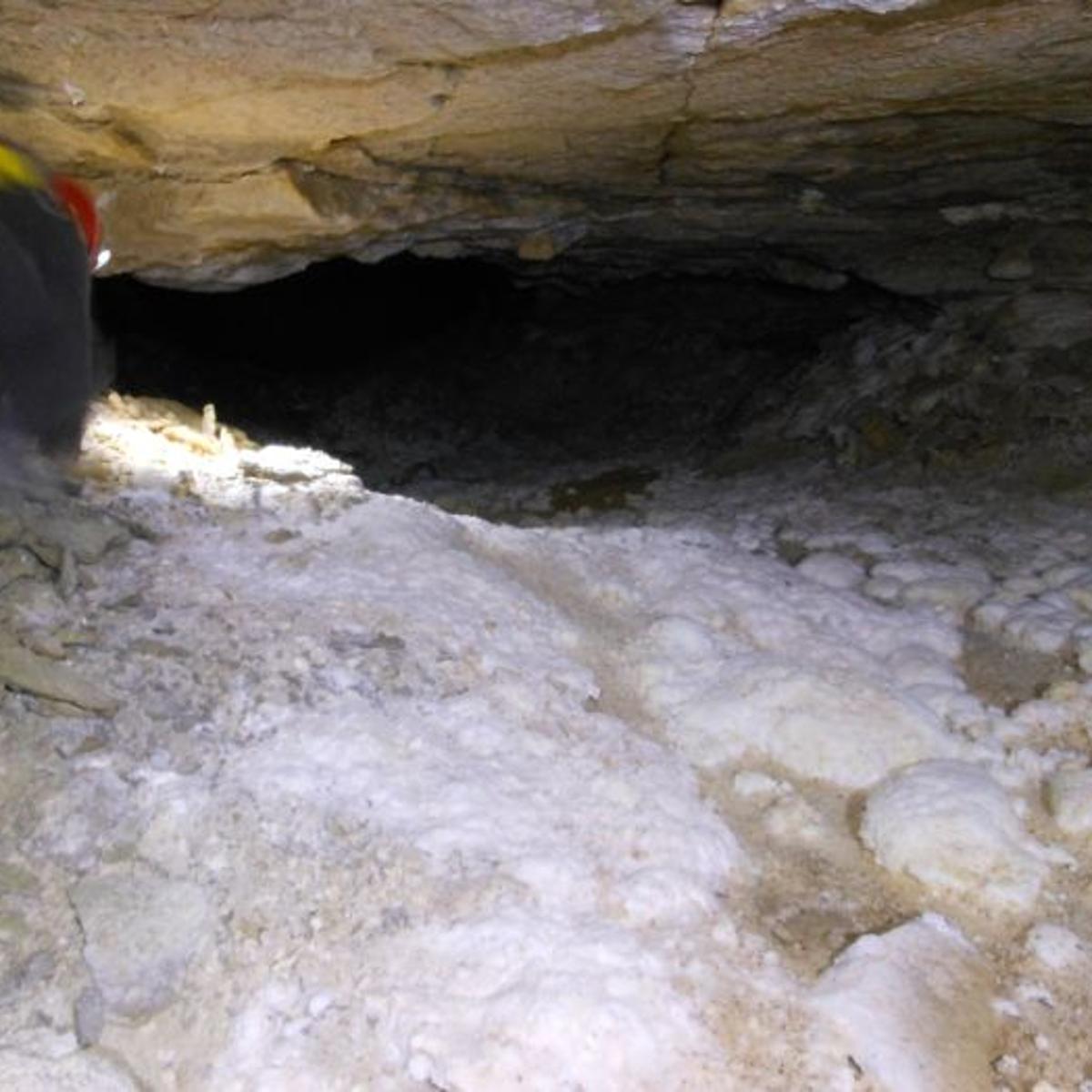

Royce Cave Billingsgazette Com

Ryan Mcginley Moonmilk Series Pretty Pictures Photo Beautiful Photography
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq4c7vpxkfmwrvau1vos0mos75kpvmm Utbbiuz Xmbmuzikq15 Usqp Cau

Monday Cave Caves Of Ireland
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqsckihe5d3bkb0zu1vcgdtdf4ueowmwp5mpa 65g6f2k3cpout Usqp Cau
Top A Carbonate Speleothem Known As Moonmilk With A Cream Download Scientific Diagram

Oregon Caves National Monument Howstuffworks

Skiing The Planet August 18

Moonmilk Cave Photo



